
Over the last 800,000 years, carbon dioxide levels have fluctuated between 180 and 300 parts per million. This current level is unprecedented and is likely to increase. The only difference is the rise. There are many things that can influence climate.
According to a recent study, the earliest known carbon dioxide levels were not more than 10 times higher than now. They may have been around 50 million year ago. The CO2 levels were comparable to today's and the climate was much more warm back then.
Although it is evident that CO2 has a significant greenhouse effect, it is also important to remember that temperature plays a major role. For over a century, scientists have been studying the Earth's atmosphere. In fact, over 800,000 years, we know the composition. The relationship between temperature and CO2 is still not fully understood. This research team developed a new method for estimating CO2 levels from the distant past.
The technique involves determining the ratio of boron to calcium in the shells of ancient single-celled marine algae. Tripati's team compared the rates of boron, calcium, and over 1,000 years to determine the amount carbon dioxide in the atmosphere. The carbon dioxide level in the atmosphere was around 280 parts/million at the time.
Tripati's team will continue pushing the record back for the next 20,000,000 years. They anticipate being able to accurately estimate the carbon dioxide levels over the entire era. If this method is successful, we could finally understand the role of CO2 in global warming.
The data can then be integrated with Earth-system models to obtain the most complete understanding of the exchange of carbon dioxide within the atmosphere. Data assimilation integrates simulations with real measurements to create the most realistic picture possible of the atmospheric exchange of carbon dioxide.
OCO-2 satellite (launched in 2014) is designed to measure atmospheric Carbon dioxide at regional scales. Until now, measurements were taken using ground-based sensors. These methods have been widely employed for decades to track CO2 levels rising.
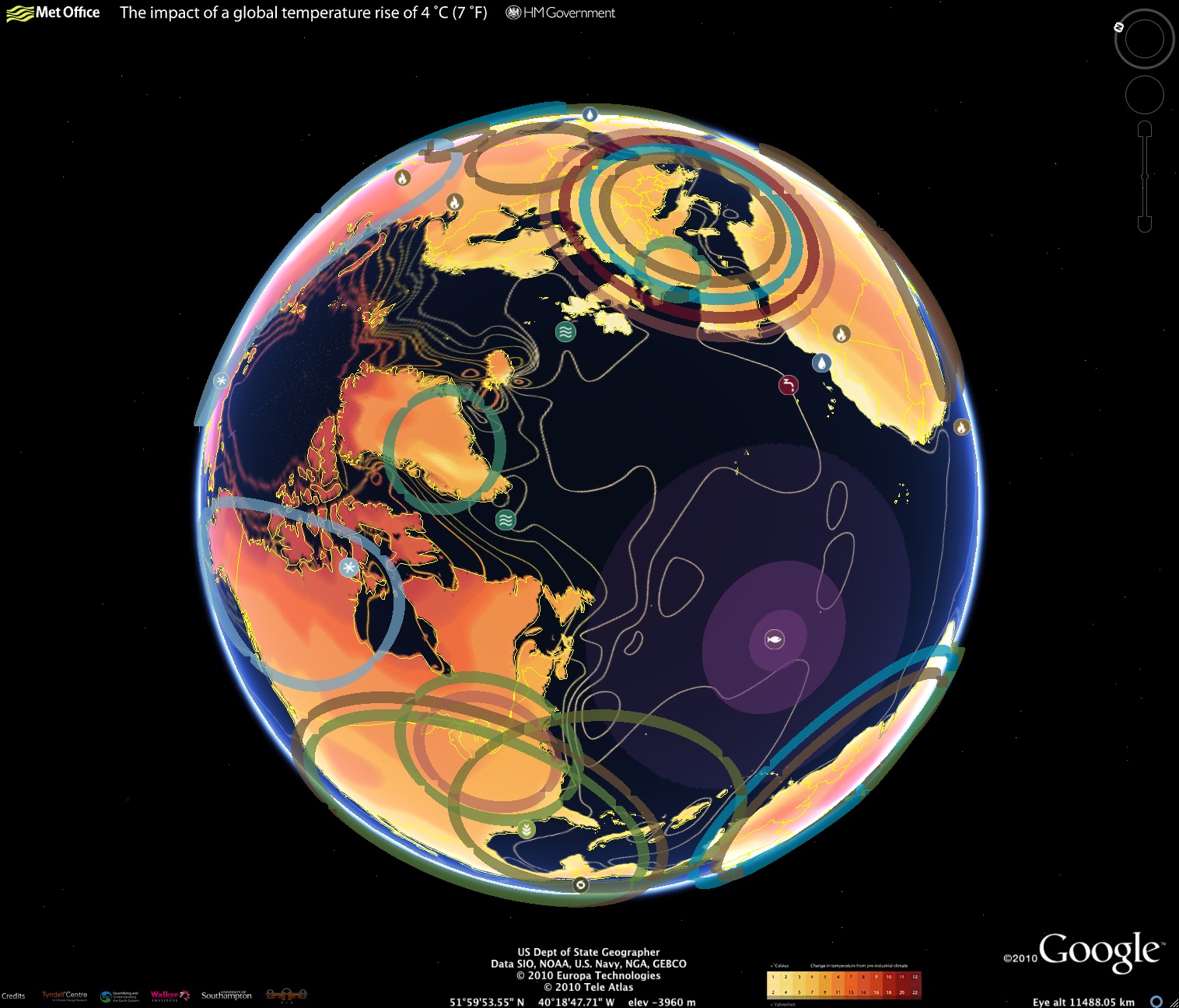
As the Earth heats, CO2 levels will rise. It is predicted that the average atmospheric carbon level will increase from 600 parts per million to 600 parts by the 21st Century. Over the same time, the oceans will heat by 0.2C per decade. Because the ocean absorbs more heat that land, it is a key contributor to global climate change.
Nevertheless, the US Energy Information Administration has reported that fossil fuel consumption has fallen in western nations by nearly 47% over the past two decades. Although it's a small drop in the bucket this is a strong indicator of what's to come.
While the global temperature is not rising over the past decade however, the levels of carbon dioxide have been rapidly increasing. Unless action is taken to slow CO2 emissions, we will see a further rise in our carbon dioxide levels.
FAQ
How are extreme weather events related to climate change?
Global warming has directly affected extreme weather phenomena such as heatwaves. Global warming has led to increased atmospheric temperatures.
Climate scientists claim that the frequency of extreme weather related disasters has more then doubled since 1980. As sea temperatures rise, so do wind patterns. This affects the normal distribution of storms and hurricanes in different geographical regions across the planet.
The 2015 El Nino event caused warm water to move towards South America, leading to rising temperatures at alarming rates and heavy rains that caused floods in Peru (and Bolivia) causing property damage and displacement. Many places, including Antarctica had their highest-ever temperatures. This suggests a connection between global warming trends or the occurrence or frequency in extreme weather events.
Another example is Hurricane Irma. In 2017, it caused $50 billion of economic losses not just in Florida, but also in other states like Puerto Rico, Cuba and Puerto Rico. This shows that climate change is responsible again for the dramatic rise in major storms.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) concluded that human activities are increasing the severity of current climate change which naturally leads to more frequent, severe, and intense natural disasters globally hence bringing forth strong evidence regarding humans' relation to extreme weather events occurring at frequent intervals around us all.
What role do greenhouse gases play in climate change?
Climate change is driven by greenhouse gases. They act like an invisible blanket surrounding the Earth, trapping the infrared radiation that warms it and keeping it from getting too hot. Without them, our planet would be much cooler than it is now.
These greenhouse gases are created by human activity such as burning fossil fuels. These activities are increasing in number, which means that more heat is trapped in our atmosphere. This can lead to extreme weather events and rising temperatures.
The most prevalent greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide, which is released from fossil fuels, such as oil, gas, and coal. Important contributors are also methane and nitrousoxide (N2O), as well fluorinated gases (Fgases).
Since preindustrial times, the concentration of greenhouse gases has risen significantly due to human activity. Global warming has caused an increase in temperature all around the globe, and in our oceans. It is also causing drastic changes, such as increased storms, droughts, melting glaciers and rising ocean levels.
Humans must reduce greenhouse gas emissions to avoid further climate change damage. This can be done by switching from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. We can also take measures such as reforestation or adopting agricultural methods that allow the soil to absorb more CO2 from the air. These activities will lower the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gasses and make the Earth a more healthy place for all life.
What is climate and how does it affect us?
Climate change refers to the long-term shifts in global weather patterns that are caused by an increase in greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, causing global temperatures to rise which leads to an array of changes in weather and climate. This could lead to rising sea levels, melting glaciers and extreme storms and dry spells, widespread coral reef bleaching, and the extinction of species.
The main cause of climate change is human activity such as burning fossil fuels for electricity and transportation, cutting down forests, and farming livestock. These activities cause the atmosphere to heat up much faster than natural processes, like volcanic eruptions. They also emit many times more carbon dioxide than volcanoes.
Global greenhouse gas emissions are also influenced by deforestation, which contributes about 15-20%. Deforestation is when trees are cut down and burned. This releases carbon dioxide from the trees back into the atmosphere. Additionally, forests act a natural carbon source that absorbs CO2 into the atmosphere. Without this capacity, carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere will continue to rise with devastating effects for ecosystems around world.
The release of CO2 into the atmosphere is not the only effect of human-caused polluting. Other harmful gasses like methane, CH4, and nitrous dioxide (N2O), are also emitted by humans. Industrial processes have used methane extensively and it contributes to significant atmospheric warming. However, N2O is emitted mostly by agricultural soil management activities such as fertilization and tilling. These activities release excessive nitrogen into the soil which leads to N2O production when microbial contact occurs.
To reduce climate change, humanity must unite efforts across the political, social, and economic systems to reduce emissions dramatically and move away from our dependency on fossil fuels toward renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power or low-carbon hydrocarbon fuels. The smart solution to reduce CO2 accumulation and atmospheric pollution could be replacing polluting fossil energy sources with zero-waste solutions. It is possible to reduce our environmental footprint by taking responsibility. Conservation measures such as reforestation can help protect biodiversity and absorb large amounts of CO2 into the environment. This will be a powerful tool in helping to solve the climate crisis and restore balance for future generations.
What are the ways climate change can be mitigated or reduced?
There are various measures that can be taken to reduce and mitigate the effects of climate change. There are many ways to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. These include using more sustainable energy and alternative sources of power. Protecting forests and wilderness habitats. Investing in sustainable transport systems. Strengthening early warning systems for natural disasters. Creating a research program about the impacts of climate change on biodiversity. Investing in green technologies like solar panels and wind turbines. Developing sustainable consumption habits and implementing appropriate environmental regulations in all areas of society. It is important to increase public awareness about climate change as it makes people feel accountable for their actions.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
External Links
How To
How to make Your Home more Energy-Efficient and Reduce Climate Change
Your home's energy efficiency is one of the most cost-effective ways to cut your carbon footprint, lower your utility bills, and improve your quality of life.
You must ensure that your home is properly insulated. Check for drafts, ensure doors and windows are properly installed, and then seal any gaps or cracks with caulking.
To maximize energy efficiency, insulate your ceilings, walls, and floors. Make sure to inspect the attic and any other areas in your home for air leaks.
Lighting can account for as much as 18% of household electricity consumption. Make sure to switch to LED bulbs, which consume up to 80% less electricity compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. Additional money can be saved by installing motion sensors, timers, and turning off lights only when needed.
It is possible to reduce your energy costs by replacing an old boiler or furnace. Newer models are more efficient. A programmable thermostat can be used to set temperature settings based on the time people are at home and away.
Switch out all old windows with new double-glazed ones which provide better insulation and don't allow heat to escape through them. Look into buying low-flow showerheads which reduce water consumption while maintaining adequate pressure levels.
ENERGY STAR-rated appliances can be replaced with products that use 50% less electricity than non-certified models. Don't forget about small details such as unplugging electronic devices like phone chargers or TV boxes when not in use - this could save you a significant amount of energy over time!
These simple steps can reduce your impact on the climate and help you live more efficiently at home.