
Africa is one of most vulnerable continents to Climate Change. Climate Change financing is essential to ensure climate-resilient green economic development. It provides financing for adaptation or mitigation projects. These requirements can be met via domestic revenue mobilization and international private financing. There is also a growing interest in regional carbon pricing initiatives. The East African Alliance on Carbon Markets and Climate Finance has expressed interest in implementing such initiatives.
Climate Change is particularly significant in Sub-Saharan Africa (SSA), where the population is already exposed to high levels of undernutrition. Its rainfed agricultural systems are particularly vulnerable to climatic changes. Furthermore, there is a growing rural-urban migration trend that adds to the urbanization trend in the region. A large portion of the population in the region relies on ecosystem services. Despite this, the SSA is the least emissions-intensive continent in terms of greenhouse gas production. This does not address the full effect of Climate Change, which has a negative impact on human existence and natural systems.
Climate change is expected to alter rainfall patterns, storm intensity, and hydrological regimes. Estuaries will also be affected by freshwater runoff and hydrological changes. These changes could increase existing anthropogenic tensions. So adaptation and mitigation should consider the abiotic consequences of Climate Change, as well as existing anthropogenic forces. Under a warming scenario of 4 text-degrees Celsius, the SSA could see sea level rise up to 1 meter by 2100.
It is essential to determine the vulnerability of South African estuaries in relation to Climate Change to aid in developing appropriate adaptation and mitigation strategies. This study identifies key stressors and potential impacts on estuaries that could be linked to Climate Change.
The key climate change stressors are an increase in sea level and decreases in rainfall and sea-ice cover as well as a shift of wind and temperature regimes. These changes are likely not to have a positive impact on estuarine systems, such as nutrient and biochemical fluxes, salinity regimes, salt regimes, and mouth condition. Due to the interplay of land and sea processes, estuaries are dynamic and can vary greatly from one area to another. A spatial resolution is required for vulnerability assessments that take into account topography and coastal biology.
This study assessed the projected vulnerability of estuaries in South Africa at the near-future (2035-2035), mid-future (2036-2065) and far-future (2066-2099) timescales using statistical models and a Coordinated Regional Downscaling Experiment. The results showed that a small increase of inter-annual variability would result a decrease in freshwater flow to estuaries. Nevertheless, KwaZulu - Natal's coast saw an increase during summer extreme precipitation.
Numerous studies have been carried out to assess South Africa's vulnerability to climate changes. These studies rely on statistical models and coastal topography, as well as coastal abiotic drivers. However, this review requires a more thorough and consolidated overview.
Estuaries not only provide essential habitat for coastal birds, but they also serve as important feeding and nursery grounds to migrant birds. They are also highly productive habitats that provide food for fish, shrimp, or other aquatic animals.
FAQ
How does climate politics affect global efforts for its resolution?
Climate change is a highly politicized issue that has created a great deal of division among nations, governments, and individuals. The political positions of various actors have an effect on the implementation and effectiveness of measures to combat climate change. It has become increasingly difficult to come to an agreement on how to address this urgent environmental crisis globally.
Scientific consensus is unanimous that human-caused climate change is real and needs to be addressed. The politics surrounding these issues often undermines global cooperation which is needed to make effective progress in implementing sustainable energy practices, upholding regulations protecting natural habitats, researching viable technological solutions, and other climate change interventions.
Many governments around the globe want to protect business interests and enforce policies that restrict business activities. This often clashes with regulations that experts recommend for effectively addressing climate change. It is very difficult for any one state or group of countries to effectively address climate change without strong commitments from all participants and broad-scale international action.
The difficulty of reaching a full consensus about the best way to combat climate change is further complicated by differences in power dynamics. Countries with more economic power frequently appoint their own representatives for international negotiations over the environment. This can lead lopsided discussions between countries' perceived interests and those of all other parties. In addition, potential side effects from implementing radical changes such as geoengineering have been debated heavily at both national and international levels.
In the same way, grassroots movements are fighting powerful opponents at the grassroots level. These include corporate ownerships and well-funded lobbyists looking to retain politically favorable positions.
If we are to achieve a coordinated effort to address our current environmental crisis, it is crucial to properly distribute resources and be aware of political divisions among nations.
What are the current international efforts to combat climate change?
The international effort to tackle climate change has reached a new level of unity and momentum. International efforts to address climate change are being facilitated by countries around the world, who are increasingly working together to reduce carbon emissions, improve resilience and invest in renewable energies.
At the global level, the Paris Agreement has galvanized collective action and serves as a framework for individual countries to set voluntary targets for reducing emissions. The UN Framework Convention on Climate Change is also providing guidance to policy and piloting innovative initiatives, such as carbon market mechanism.
Progress is also being made in specific regions; for example, The European Green Deal is a comprehensive package of legislation aimed at recreating Europe's economy with sustainability at its core, while countries of the African continent have committed to the African Renewable Energy Initiative which aims to increase Africa's share of global renewable energy production.
Apart from policy changes, action is visible across sectors and industry. Cities are actively transitioning to sustainable public transport systems. Society at large is adopting more sustainable lifestyles. Companies have been innovating technologies to lower emissions. Investors are switching away from fossil fuels to invest in renewables.
The OECD committee's wealthy members have adopted common standards in reporting on national actions related to climate change. These are the Common Reporting Frameworks (CFR), also known as the 2021 Guidelines.
All these efforts are a sign of the unprecedented importance given to climate action. Governments, civil society & private sector stakeholders alike must continue to build upon the momentum and push towards even greater ambition & progress if there is any hope of meeting Climate goals set by science & enshrined in international law.
What is the current status of the global climate, and how is it changing in the future?
The global climate is currently experiencing unprecedented uncertainty and change. Unprecedented atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide are leading to significant temperature increases, including droughts, heat waves and changing rainfall patterns. They also cause ocean acidification, rising sea levels, and melting polarice caps.
These changes are already having a profound impact on ecosystems around the world, causing extinctions and disruption of habitats. They are also threatening millions of people's lives and livelihoods, particularly in areas where there is already resource scarcity.
Human activity has led to an increase in extreme weather events such as hurricanes, cyclones, floods, wildfires, etc. As temperatures continue their climb, this trend is expected to continue.
A rapidly changing climate has many effects. They can impact everything from food insecurity to displacement by extreme weather events to sea level rise, causing communities to relocate. Climate change is also increasing social inequality bydisproportionately impacting marginalized communities who lack the necessary resources and knowledge to adapt.
While progress has been made in some countries in terms of reducing carbon emission or developing renewable energy programs, there has yet to be any meaningful action taken at a global scale that would allow us to address these issues effectively. We must all work together now to stop further disruptions and destruction from climate change.
What are the implications of climate change for the environment and society?
Climate Change has broad effects on both the environment and society. Rising global temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and decreased air quality are just some of the environmental impacts of climate change. These changes can have serious implications for human populations, creating instability in communities, intensifying poverty and insect-borne diseases, altering human migration patterns, and destroying vital habitats.
Already, climate changes are having wide-ranging and profound effects on the environment worldwide. As global temperatures rise, this trend is likely to intensify in the near term.
One of the most prevalent effects of climate changes worldwide is the rise of ocean levels as a result of melting ice cap. This results in coastal erosion and increased flooding risks for coastal communities. Saltwater intrusion can also happen, affecting freshwater supplies to coastal regions of many countries.
Due to climate change, extreme weather phenomena such as heatwaves/droughts frequently occur across many countries in the world. These events cause mass destruction to homes and businesses, leading to displacement or relocation of communities or wiping out whole towns in some cases. In addition, intense storms create further risks related to flooding or landslides that increase damages to infrastructure such as roads and railways.
Wildfires caused by climate change also increasingly occur more frequently than they did before with devastating results both for habitats and people living nearby who may find their lives at risk due to poor air quality when these fires spread smoke across affected areas.
This drastic change in living conditions is often a result of displacement or even refugee situations. When people decide to leave their homes, either involuntarily or voluntarily, it can be because their town has become too dangerous or not habitable due the changed climate conditions.
Increased aridity also increases dust storms worldwide with unhealthy air pollution caused by these making it difficult for people who suffer from respiratory illnesses such as asthma especially vulnerable. Pest infestations will increase due to higher temperatures - a phenomenon called the 'greenhouse bug'. This can further impact global food insecurity as fewer crops are available with poorer nutritional qualities, potentially creating additional hardships for marginalized populations that otherwise would be barely able to make ends meet.
What role do greenhouse gases play in climate change?
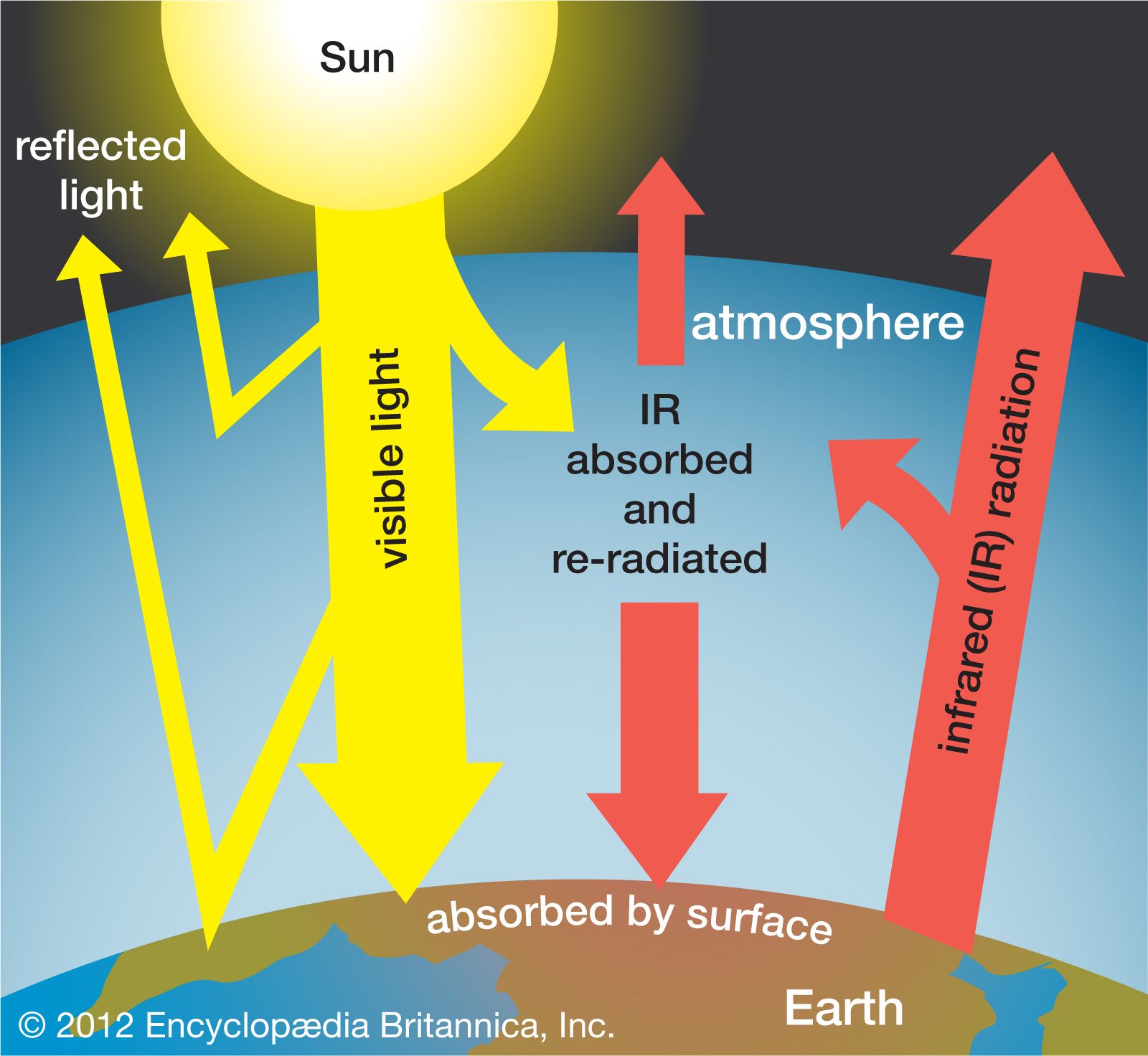
Greenhouse gases play a major role in climate change. They act as an invisible blanket that wraps around the Earth, trapping heat radiation and warming it. Without them the planet would be much more colder than it currently is.
These greenhouse gases are created by human activity such as burning fossil fuels. As more heat enters the atmosphere from these activities, it leads to increased temperatures and extreme weather.
The most abundant greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide (CO2), which is released when burning fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and gas. Major contributors to climate disruption are methane (CH4) as well as nitrous dioxide (N2O) and fluorinated gases (F-gases).
Human activities have caused a significant increase in greenhouse gas concentrations since preindustrial times. This has led worldwide warming and increased temperatures in the oceans as well as all over the planet. It is also leading to changes such as intense storms and droughts; melting glaciers; and rising seas.
Humans must reduce greenhouse gas emissions to avoid further climate change damage. This can be done by switching from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power. We can also adopt reforestation methods or agricultural methods that allow the soil absorb more CO2 in the air. These activities will reduce atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations and create a healthier environment that supports all life.
Statistics
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Invest in Clean Energy, and Support the Transition to Low-Carbon Future
Clean energy refers to any type of renewable energy that does no polluting or emit carbon dioxide, as well as other greenhouse gases. It includes technologies such as solar photovoltaic, wind power, hydroelectricity, geothermal energy, and hydrogen fuel cells. Renewable energy sources have many environmental benefits. This includes a decreased reliance on fossil oil, a decrease in air pollution caused by traditional electricity methods, as well as providing reliable electric access to remote locations.
Shares in companies developing innovative technologies in clean energy can be purchased by investors. This includes investing directly in stocks, mutual funds, ETFs, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) related to clean energy. Investors may also be interested in direct investments in start ups or venture capital projects that fund research and technology development.
Clean energy investors support innovation that reduces harmful emissions from electricity generation. This investment may also lead to increased economic development by creating jobs related to the production of renewable energy systems that require skilled labor and engineers. Lastly, investors may see a return on their investment in clean energy through tax incentives programs. These incentives encourage green technology investments such as solar panels, wind farms, and biomass heat production systems.
We can help the transition to low-carbon by investing in companies that create electricity from renewable resources.