Clean Air Act creates legal mechanisms for addressing the problem of pollution from transport. However, Congress didn't explicitly give States the authority to act according their own deadlines. EPA therefore developed a policy that will resolve the tension between deadlines. This policy has been designed to give upwind areas the opportunity to assume responsibility for pollution. EPA is following Congress's directive.
The EPA's Attainment Date Extension Policy is an appropriate interpretation of the Clean Air Act provisions. EPA understands that attainment for upwind areas is not as easy as it would be for them to do so as quickly as they wish. EPA has extended the attainment deadlines to upwind areas in an effort to achieve this goal. The NOX submission extension was also limited to areas with known transport problems. If an upwind area fails to achieve its goal, it may be required to take more stringent controls.
Until late 1998, EPA could not allocate responsibility for transport. EPA however had a sufficient understanding about the scale and extent of the transport pollution problem. Even after this, EPA was unable to get adequate redress for transported pollution until the OTAG process was completed. EPA interpreted section 181(a), Clean Air Act, according to its understanding of the transport pollution problem.
The EPA's Attainment Strategy and Guidance states that the transport of pollutants is an integral part the nonattainment of an area. A state in the upwind cannot rely on segregation or emissions to attainment. EPA was unable to assess the suitability of control measures by upwind states.
EPA gained a better understanding of the transport polluting problem in early 1999. EPA had analyzed regional transport pollution and associated air pollution, and found that pollution from upwind areas was most likely to be transported to their downstream areas. The states and EPA collaborated to determine who was responsible for transport. An initial regional transport analysis, which took years to complete, was conducted. In 1999, EPA officially announced the transfer of transport responsibility. EPA admitted that it was difficult for them to create a comprehensive approach because they didn't have a clear understanding of how to measure the emissions.

EPA responded to critics of the EPA's Attainment dates extension policy. While EPA believes it is in accordance with Congress's intent the policy has been criticized by those who claim it does little to provide relief for areas upwind. EPA believes the policy should only ever be applied as a last option. Despite the EPA's recognition of the importance of the graduated attainment framework, EPA has not changed its position on the reclassification provision.
Although EPA reclassified Phoenix in moderate conformity with section 179B, it was not meant to be a punitive step. Instead, it was designed to protect downwind regions from the transport polluting problem. Section 181(a) of the Clean Air act directs the classification of ozone nonattainment areas based on design values. EPA and states collaborated to address transportation issues during the OTAG process.
FAQ
What can we do to help the climate change process?
Climate change is a major contributor to human activity. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, humans have contributed more than 70% of global warming since mid-20th century.
Burning fossil Fuels: The atmosphere is effected by the combustion of fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas. This raises the already existing atmospheric levels of CO2 which acts as an "greenhouse gas", trapping heat from Earth's surface and increasing temperatures. This leads to higher ocean levels as Arctic ice melts and scrambles weather patterns around the world leading to deadly storms, droughts, and floods which could affect food production and endanger human health.
Deforestation. Trees that absorb atmospheric carbon dioxide from the atmosphere in photosynthesis will be effected by being cut down. The albedo is also increased by cutting down forests. It refers to the amount of solar radiation reflected back into space. As well decreases local air quality with deforestation being linked permanently with respiratory issues.
Farming is responsible for 14% to 18% of all anthropogenic greenhouse emissions globally each year. Because of its high methane content, animal waste emits large amounts methane into the atmosphere. Reducing your intake of animal products is an effective way to lower your greenhouse gas emissions. Nitrous oxide can also be released into our atmosphere. This creates smog that harms our respiratory system.
In conclusion, although human activity has had a devastating impact on our environment for centuries, technological advancements have enabled us to focus our minds towards the future. Instead of relying on carbon-emitting heavy industry, we can use green innovation to create eco-friendly efforts that combat climate change effectively and ensure everyone's safety.
How can climate change be mitigated or reduced in its impact?
There are various measures that can be taken to reduce and mitigate the effects of climate change. These include reducing greenhouse gas emissions through better energy practices and using alternative sources of energy such as renewable resources, employing more efficient agricultural techniques, improving land management practices, enhancing air quality laws, protecting forests and wilderness habitats, protecting against extreme weather events such as floods and droughts, investing in sustainable transport systems, strengthening early warning systems for disasters, beginning a research program on the impact of climate change on biodiversity and ecosystems, investing in green technologies such as solar panels or wind turbines, encouraging sustainable consumption habits, implementing suitable environmental regulations across all sectors of society. It is important to raise awareness of climate change in order to encourage people and make them feel responsible for their actions.
What are the impacts of climate change on biodiversity, ecosystems and species?
Climate change can have a variety of impacts on biodiversity, ecosystems, and the environment. Climate change is affecting ecosystems and wildlife today.
These changes can result in shifts of habitat areas, disrupting food chains or affecting population numbers or distributions. With potentially devastating consequences for biodiversity, ecosystems and their functioning, these shifts in climate conditions could cause significant impacts. Hydrological changes can also impact water availability for aquatic species.
Climate changes can lead to higher temperatures and more frequent extremes (such as droughts) which put more stress on already fragile systems, like coral reefs or tropical forests. The climate change will lead to the extermination or decline of as many as 30% of animal species in 2050. This could cause further destruction of ecological communities.
Climate change is an enormous threat to biodiversity and to human societies which depend on functioning ecosystems. The best way to minimize its impact is to work at every level to reduce global warming trends. Future damages can be avoided with prudent management practices.
What role do greenhouse gases play in climate change?
Climate change is influenced by greenhouse gases. They act like an invisible blanket around the Earth, trapping infrared radiation and warming the atmosphere. Without them, the Earth would be much colder today than it is today.
The human activity of burning fossil fuels, or other industries that generate emissions, can create greenhouse gases. As these activities continue to increase, more heat gets trapped in the atmosphere, leading to rising temperatures and extreme weather events.
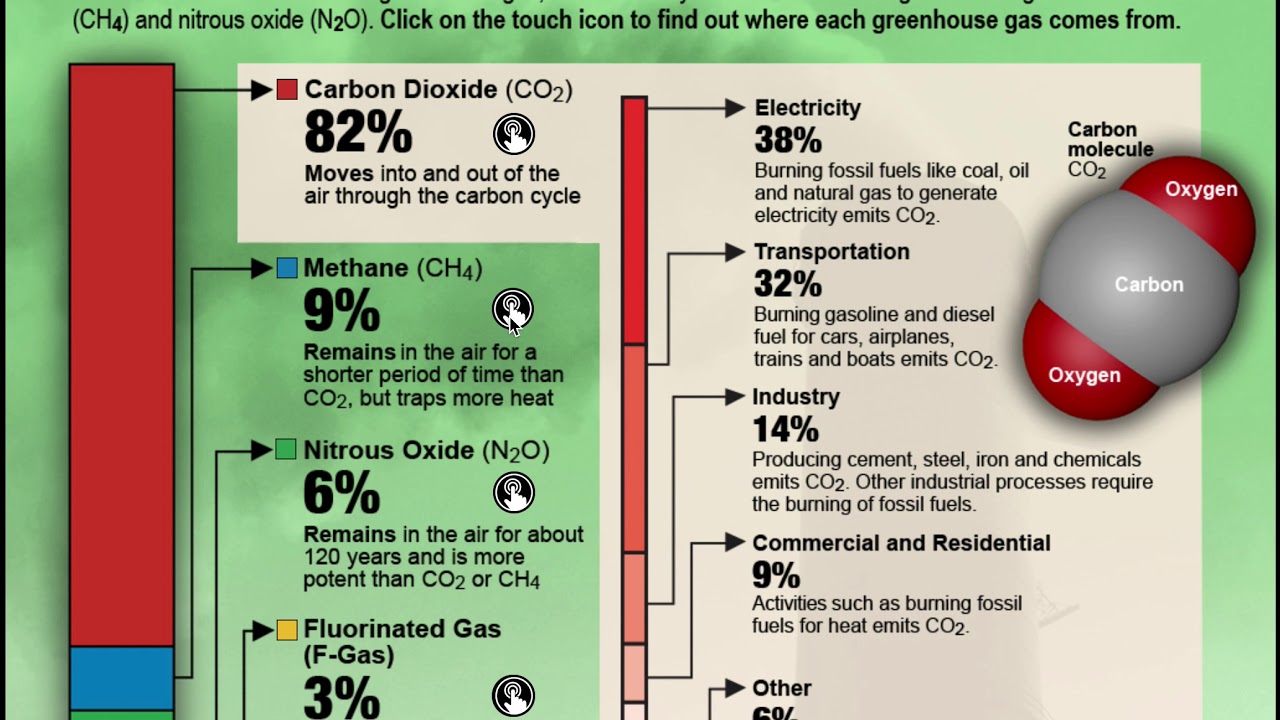
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most common greenhouse gas. It is produced when fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas are burned. Other major contributors to climate changes include methane, nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases (F-gases).
Because of human activities, the concentrations of greenhouse gases have increased substantially since preindustrial days. This has led worldwide warming and increased temperatures in the oceans as well as all over the planet. It is also causing drastic changes, such as increased storms, droughts, melting glaciers and rising ocean levels.
To reduce further damage caused by climate change, human beings need to decrease their greenhouse gas emissions. We can do this by shifting away from fossil fuels in favor of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power. We can also adopt reforestation methods or agricultural methods that allow the soil absorb more CO2 in the air. These actions will help reduce atmospheric concentrations in greenhouse gases and create a healthier ecosystem for all life.
What can be done to ensure a sustainable future, given the climate change challenges?
Sustainability refers to the ability to satisfy current needs while not compromising future generations' ability to do so. An urgent need exists to act to eliminate our dependency on finite natural resources and to shift towards a more sustainable method of using them.
In order to create a more sustainable world, we must change our consumption patterns and production methods. We also need to consider our dependence on natural resources, such as fossil fuels. We must look for new technologies and renewable sources of power, as well as systems that lower harmful emissions and still provide our daily needs.
Furthermore, it is crucial to take a holistic approach to sustainability. This includes all aspects of production including materials, waste management and reuse strategies as well as energy usage in transport and industry. There are many options available, including the use of renewable energies like solar, wind and hydropower, improved waste management systems, increased efficiency in agriculture, improved transport networks, green building regulations, and sustainable urban planning.
To achieve this goal, we need to make behavioral changes in order for people from all walks of society to be successful. Education programs will be needed to support individuals in understanding climate change and how they can positively contribute towards a sustainable world.
Ultimately, only through collaboration between governments, industry leaders, and citizens will we be able to make significant progress in creating a more sustainable world for generations to come.
What is the state of international efforts for climate change mitigation?
International efforts to combat climate change are moving at a remarkable pace and with unprecedented unity. Countries all over the world are now working together to reduce emissions, improve resilience against impacts, as well as invest in renewable energy sources.
The Paris Agreement has energized collective action at the global level and is a framework that allows individual countries to set voluntary emissions reduction targets. Additionally, the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) is providing political guidance and piloting new initiatives such as carbon market mechanisms.
Other regions are seeing progress. The European Green Deal is a comprehensive legislation package that seeks to create a European economy with sustainability as its core. Countries on the African continent also have committed to The African Renewable Energy Initiative, which aims increase Africa's participation in global renewable energy production.
Along with policy changes, action can be observed across all sectors and industries. Cities are actively moving toward sustainable public transport systems. Society as a whole is moving towards more sustainable lifestyles. Companies invent technologies that reduce carbon emissions. Investors are shifting their capital away to renewables.
The OECD committee has adopted common standards to report national actions on climate change by rich countries. This is known as the 2021 Guidelines.
All of these efforts show an unprecedented focus on climate action. To meet climate goals, both governments and civil society must continue to build on the momentum.
What is the potential impact of land-use change and deforestation upon climate change?
Deforestation, land use change and other factors have an immediate and direct impact on climate. Trees that are cut down or burnt can no longer absorb carbon dioxide. This is one of the most important greenhouse gasses on Earth. Carbon dioxide is therefore less removed from the atmosphere when trees are deforested or burned for agricultural purposes.
Land use changes can also increase the atmospheric concentration of greenhouse gases. The use of fertilizer and pesticides can also increase the emissions of methane and nitrogen oxide when forests are replaced by agricultural lands. Clearing can also increase soils with high levels of carbon stored in them; these soils can be disturbed or turned over by farming activities and release more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
The effects of land-use change, deforestation, and increased greenhouse gas emissions can have a negative impact on the quality of regional air. Smoke from deforestation-related burning events has been shown to cause decreased visibility and health problems such as asthma, as well as other respiratory conditions. The global climate can change as a result of changes in local air quality. This is because more sunlight reaches the Earth's surface than the atmosphere.
Deforestation and changes in land use have contributed significantly to the increase in global greenhouse gas emissions. They also have had adverse effects on local air quality, which further contributes to climate change. If serious efforts to mitigate climate change are to be made, it is important that these practices are reduced.
Statistics
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to make your home more energy-efficient and combat climate change
Making your home energy-efficient is one of the best ways to reduce your carbon footprint, save money on utility bills, and make life more comfortable.
Start by ensuring your home is properly insulated and sealed. You should ensure windows and doors are correctly installed, check for drafts around pipes, vents, and add weather stripping where needed.
Insulate your floors, ceilings, & walls for maximum energy efficiency. Inspect your attic for any air leaks or areas that aren't well-insulated.
Lighting can account for as much as 18% of household electricity consumption. Make sure to switch to LED bulbs, which consume up to 80% less electricity compared to traditional incandescent bulbs. Additional money can be saved by installing motion sensors, timers, and turning off lights only when needed.
An old boiler or furnace can be replaced to save money on energy. They are also more efficient. A programmable thermostat can be used to set temperature settings based on the time people are at home and away.
Switch out all old windows with new double-glazed ones which provide better insulation and don't allow heat to escape through them. Low-flow showerheads can be purchased to reduce water consumption, but still maintain sufficient pressure.
ENERGY STAR rated devices use 50 % less energy than non-certified appliances. Do not forget to unplug electronic devices, such TV boxes or phone chargers, when not in usage. This can help you save considerable energy.
These few simple steps will make your home more energy efficient and reduce your carbon footprint.