Climate change mitigation is a term that describes the actions taken to prevent climate change. These actions include reducing greenhouse emission, removing air pollutants, and improving efficiency. The first workshop, held in April 2019, was designed to identify the various mitigation options that could potentially be employed to address climate changes.
A second workshop, which was held in October, was designed to evaluate the health effects of demand side mitigation options. An extensive literature review was performed to support this goal. This reviewed a variety of approaches to evaluate the relationship between climate change mitigation and well-being. The work was done by a team of experts that included well-being experts and technology specialists, along with other professionals. The cobenefit approach was used to assess the wellbeing of the scenarios.

Demand-side solutions are aimed at modifying the choices of consumers and businesses by changing the demand for goods and services. They are different than supply-side approaches, which aim to change production processes and production technologies. Examples of demand-side strategies include increasing the adoption of sustainable practices, and promoting sustainable land use and forests.
There are several types of demand-side solutions. The category "shift" refers to a strategy that shifts to low-carbon technologies. Some of these strategies include increasing the availability of electric vehicles, developing more sustainable transport, or reforestation. Some strategies focus on reducing unnecessary consumption. It is important to model more behavioral consequences of such actions.
While most research has been conducted from a macroeconomic perspective, the social dimensions are often overlooked. More research should be done to understand how people's preferences, beliefs, and worldviews affect their decisions and the effects of climate change mitigation measures on their well-being. Research is needed to examine the relationships between the many mitigation options and their social constituents, such as people’s economic and personal wellbeing.
The joint evaluation of climate mitigation and well-being has three main limitations. The first is that the eudaimonic approach to climate change mitigation, which emphasizes the substantive conditions necessary for a happy life, is not well represented. Second, current assessment centres on GHG emissions have been limited to a macroeconomic perspective. A third, more specific research is required to better understand the impacts of wider climate change mitigation options as well as the social constituents.
The workshop's first session was led by nine experts. They brainstormed and identified possible demand-side solutions for climate change. The participants were divided into three different groups: the industry, infrastructure, or health and wellness sectors. The upper boundaries of each area were determined in rounded numbers during the internal review.
The workshops, which addressed the wellbeing aspects of demand side mitigation options, discussed the consequences of these policies for citizens' well-being. They also considered the possibility of evaluating well being using the eudaimonic model.
FAQ
How do developing countries and communities experience the effects of climate change?
Due to limited access, technology, and healthcare systems, developing countries, communities, are particularly vulnerable to the consequences of climate change. Temperature, precipitation and sea level changes increase pressure on already finite resources. Already fragile ecosystems are being destroyed by floods or droughts. Rising temperatures can lead to a decrease in crop yields, which will disproportionately affect poorer communities struggling with food insecurity. Extreme weather events like hurricanes or heatwaves can also cause destruction to infrastructure, causing further economic inequality.
Climate change has long-term consequences. They will lead to continued resource scarcity, extreme poverty, and adverse health effects, including increased incidences of vector-borne illnesses like dengue fever and malaria. A rise in sea levels and extreme weather events will lead to increased flooding. This could put lives at risk in coastal regions, where there is often a lack of emergency services or infrastructure. These risks can be mitigated by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. However, other measures may be required such as better management of freshwater resources or easier access to healthcare facilities that aid in the prevention of diseases like malaria.
What does climate change politics have to do with global efforts to combat it?
Climate change has become a highly politicized topic that has caused great divisions among governments, nations, and individuals. Politicians of many actors influence the implementation of actions to address climate change. It has been difficult to reach a consensus on the global effort to address this urgent environmental problem.
The overwhelming majority of scientists agree with the fact that human-generated global warming is real. It is urgent for action to address it. These politics often hamper global cooperation needed to achieve effective progress in implementing sustainable energy practices.
Most governments are eager to protect their business interests and enforce rules that will limit business activity as much as possible. This is often in conflict with the regulations experts recommend to combat climate change. It is very difficult for any one state or group of countries to effectively address climate change without strong commitments from all participants and broad-scale international action.
The difficulty of reaching a full consensus about the best way to combat climate change is further complicated by differences in power dynamics. Countries with more economic power may appoint themselves to be represented on international bodies for negotiations about the environment. This can lead the to divisive discussions between the countries' interests and the collective interest. Additionally, the potential side effects of implementing radical changes like geoengineering are being heavily debated at both national as well international levels.
The grassroots movements also have struggled against powerful enemies, such as corporate ownerships and well funded lobbyists who want to maintain politically favorable positions in their industries. This includes funding research into alternative forms energy production and enforcing renewable technology mandates. It is important that individual governments are clear about the possible rewards and outcomes if they intend to actively pursue valid progress on this matter and not seek public favor through short-term gains and spectacles.
Properly distributing resources allocated towards any intervention program while being mindful of political divisions between nations will be critical if any coordinated effort aimed at mitigating our current environmental crisis is going successfully to come to fruition.
What does the role of greenhouse gases contribute to climate change?
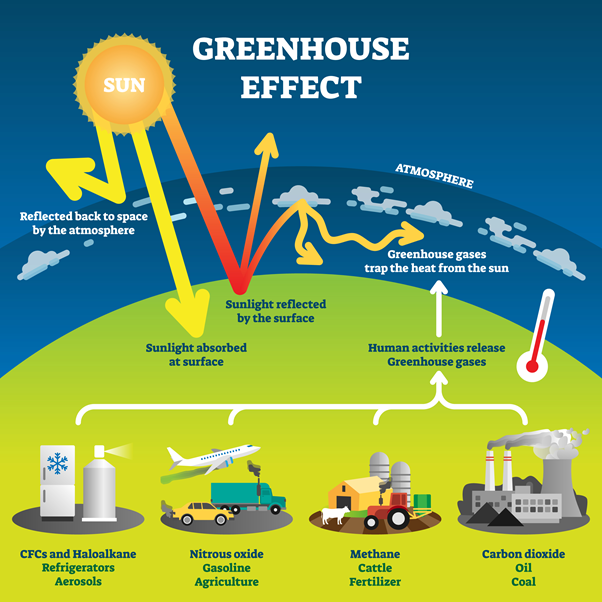
Climate change is driven by greenhouse gases. They act as an invisible shield around the Earth and trap infrared radiation, warming the atmosphere. Without them, the planet would be much colder than it is today.
Greenhouse gases are generated through human activity, such as burning fossil fuels or other industries that produce emissions. These activities increase the heat that is trapped in the atmosphere. This leads to higher temperatures and more extreme weather events.
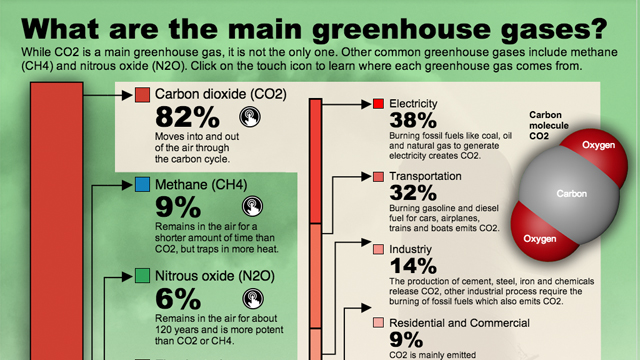
The most prevalent greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide, which is released from fossil fuels, such as oil, gas, and coal. Other major contributors to climate changes include methane, nitrous oxide and fluorinated gases (F-gases).
Human activities have caused a significant increase in greenhouse gas concentrations since preindustrial times. This has led to global warming and an increase in temperatures all over the world, as well as in our oceans. It is also causing major changes such as stronger storms and more droughts, melting of glaciers, rising sea levels, and increased flooding.
To avoid further damage from climate change, humans need to reduce their emissions of greenhouse gases by transitioning away from fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources like solar or wind power. We can also adopt reforestation methods or agricultural methods that allow the soil absorb more CO2 in the air. These actions will reduce the atmospheric concentrations and improve the environment for all living things on Earth.
What is the impact of climate change on oceans and marine life around the world?
What will climate change do to the oceans and marine life of the world?
Since its inception, climate change has had a significant impact on the oceans and marine life of the world. Constant oceanic warming due to the depleted ozone layer causes drastic disruptions in marine ecosystems resulting in a decrease in species and coral bleaching.
Climate change also causes unpredictable weather conditions and stronger storms. These extreme surges can be deadly for coastal areas. Additionally, temperature changes may cause water systems to lose oxygen. This can result in "dead areas" in which abundant marine life is reduced.
Ocean acidification can also be caused by climate change. Excess carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere and accumulates in the oceans. Ocean acidification raises the pH balance which disrupts essential functions of animals unable to adapt such as oysters, clams, and crabs as their shells become weakened.
Higher temperatures can also change the location or shrinkage of natural habitats, making them less suitable for some species. Ocean stress increases already high extinction rates worldwide, creating a severe imbalance of predators and prey which might lead eventually to complete extinction.
All ecosystems are affected by climate change. This can be directly or indirectly via evaporation, water volume reductions or sharp temperature shifts. These changes could have a devastating effect on sustainable development of marine activities and fisheries. Global climate change continues to decimate entire species, changing future lives on earth and below the surface of the oceans.
What is the current status of the global climate, and how is it changing in the future?
The current global climate state is one of unprecedented change and uncertainty. Unprecedented levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide are causing temperatures to increase significantly, leading to droughts, heat waves, changing rainfall patterns, melting polar ice caps, ocean acidification, and rising sea levels.
These changes already have a profound effect on ecosystems all over the globe, causing habitat destruction and extinctions. They also threaten the livelihoods and lives of billions, especially in areas that are already suffering from resource scarcity and poverty.
Increased average surface temperatures, which are caused by human activity, have led to an increase of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes or cyclones. As temperatures continue to rise, this trend is likely to continue.
Climate change has global consequences. It can affect everything, from food insecurity and displacement to communities that are forced to relocate due to severe weather events or rising sea levels. Climate change is also increasing social inequality bydisproportionately impacting marginalized communities who lack the necessary resources and knowledge to adapt.
While progress has been made in some countries in terms of reducing carbon emission or developing renewable energy programs, there has yet to be any meaningful action taken at a global scale that would allow us to address these issues effectively. In order for us to prevent further disruption and devastation from climate change all nations must come together and take urgent action now while at the same time planning for adaptation in an increasingly uncertain world.
What is the potential for new technologies to address climate change?
This global problem is a huge challenge that new technologies can address. Advanced science is making it possible to shift to a more sustainable world.
New methods for carbon capture or sequestration can be used to lower greenhouse gases. Additionally, improved agricultural practices can reduce the emissions of livestock and soil erosion. Smart grid technology may also be used to boost efficiency and improve building design.
In addition, cutting-edge synthetic biology approaches allow scientists to develop organisms that can utilize green sources of fuel such as CO2 laser into usable biofuel or alternate feedstock. If the market shifts away from petrol-based cars to zero-emission electric vehicles powered by clean sources, this could transform transportation.
Finally, greater investment in digital technology and AI can help empower people across borders with greater access to data on their ecological footprint and ultimately lead to more informed choices regarding consumption habits. Understanding our carbon production role is essential to help us all be better stewards.
What are the impact of deforestation and land use change on climate change?
Climate change is directly affected by land use changes and deforestation. The trees that have been cut down or burned can no longer absorb carbon dioxide, one of Earth's most important greenhouse gases. This is why less carbon dioxide is removed when trees are cut down or burned for agricultural reasons.
At the same time, changes in land use can also release more greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. To illustrate, if forests are replaced with agricultural lands to support livestock production, fertilizer and pesticide use could increase methane emissions. Clearance can increase exposure of soils that have large amounts stored carbon. These soils release carbon dioxide when they are turned over or disturbed through farming activities.
Deforestation, land-use change and other environmental impacts can cause more greenhouse gas emissions than they do. It can also affect regional air quality. The smoke from deforestation's burning events has been linked to poor visibility and other health concerns, such as asthma or other respiratory diseases. Because of the reduced amount of aerosol particles in our atmosphere, which scatter sunlight off the Earth's surface, these changes can have a cumulative impact on global climate.
Deforestation and changes in land use have contributed significantly to the increase in global greenhouse gas emissions. They also have had adverse effects on local air quality, which further contributes to climate change. If serious efforts to combat climate change are to occur, it should be a top priority to reduce these practices.
Statistics
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Invest in Clean Energy and Support the Transition to a Low-Carbon Future
Clean energy is renewable energy that doesn't emit greenhouse gases or produce polluting emissions. It encompasses technologies like solar photovoltaics and wind power. Investing in clean energy sources can bring many environmental advantages, including a reduced reliance on fossil resources, less air pollution, better electrical access, and greater reliability to remote locations.
Shares in companies developing innovative technologies in clean energy can be purchased by investors. This could be done by investing in publically traded stock, mutual funds, or ETFs related to renewable energies. Investors might also consider direct investments in start-ups or venture funds to finance research and development for clean technology technologies.
Investors in clean energy support innovation that reduces the harmful effects of traditional sources of electricity generation. This investment can also help increase economic development through the creation of jobs in the production and engineering of renewable energy systems. The tax incentives programs that encourage investment into green technologies such as wind farms and solar panels can also provide investors with a financial reward.
By investing in companies focused on creating cleaner sources of electricity from renewable resources such as sun, wind, and water while avoiding activities that could harm the environment, we can support the transition to a low-carbon future while reaping economic rewards at the same time.