
The health and livelihoods on islands are at risk from climate change. Small islands are particularly vulnerable. They are often inhospitable, have small land masses and are limited in freshwater resources. These vulnerabilities are likely to increase with the sea level rising. Many island nations have made bold attempts to increase their resilience against climate impacts. However, the international community must continue to take action to curb greenhouse gas emissions and prepare for the impacts of changing climate.
The Pacific Islands, which are smaller than other regions, face an extremely difficult challenge. The region is dependent almost entirely on imports of fuel and material. The region's airports and ports are also vulnerable to storms and wave heights. The region's ability to handle increasing storm surges as well as saltwater intrusion and sea-level rise has significantly decreased. This puts the human population at risk of severe flooding and disease outbreaks.
Many Pacific island communities have already begun to develop climate adaption plans. Hawaii, for instance, has state agencies that have developed a process for coordination of statewide climate adaption planning. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, (NOAA), has funded an island resource safety study.
Despite all these efforts, Tuvalu as well as the Marshall Islands face serious problems. Scientists have predicted that the Marshall Islands may become inhospitable within their lifetimes. Similarly, Tuvalu has begun planning for the disappearance of land. Its leaders have been fighting back against polluters and recently called on wealthy country to uphold their Paris Agreement promises.
Climate change will also affect freshwater availability and reduce the quantity of potable water for drinking. This will adversely impact the aquifer replenishment, leading to increased flooding and disruptions in public sanitation. Furthermore, ecosystems on land will be affected by changes in ocean chemical.
Low-lying islands in the Marshall Islands and Vanuatu will be especially vulnerable to coastal flooding and sea level rise. Because they have very limited agricultural resources, their population is more vulnerable to diseases caused by warm and humid weather. Many islands will soon run out of fresh water. As a result, people will have to migrate before the area becomes uninhabitable.

High-elevation isles will also have to face similar challenges. Waimea, for example, is located at a high elevation of more than 2,500 feet. It has a dry, hot winter and a pleasant summer. The island's temperature at the surface is often above 60 degrees Fahrenheit.
In the end, islands will experience a severe water scarcity. Insufficient water resources can lead to decreased crop production, reduced freshwater supplies for drinking and an increase in the incidence of disease. The history of governance and topography will also play a part in these issues.
Climate change related migration will present significant practical and economic challenges. Vanuatu's low-island community of Marshall Islands might have to move up before the seas submerge.
FAQ
What's the potential for climate-change technology?
There are many technologies that can be used to tackle this global problem. From renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and geothermal to energy storage systems like battery packs or thermal tanks, advances in applied science are making it possible for us to transition to a more sustainable future.
New methods for carbon capture or sequestration can be used to lower greenhouse gases. Additionally, improved agricultural practices can reduce the emissions of livestock and soil erosion. Smart grid technology can be integrated with existing power infrastructures to improve efficiency. Enhanced building design can help reduce energy consumption.
In addition, cutting-edge synthetic biology approaches allow scientists to develop organisms that can utilize green sources of fuel such as CO2 laser into usable biofuel or alternate feedstock. This could make transportation more efficient if the market moves away from petrol-powered vehicles and towards zero-emission electric cars that are powered by clean energy.
Finally, investing in digital technology and AI will help people from all over the world gain access to information about their environmental footprint and make informed decisions about how they consume. Understanding our carbon production role is essential to help us all be better stewards.
How does human activity affect climate change
Climate change is caused primarily by human activity. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, humans have contributed more than 70% of global warming since mid-20th century.
Burning fossil Fuels: The atmosphere is effected by the combustion of fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas. This increases the already high levels of atmospheric CO2, which acts as a greenhouse gas by trapping heat from Earth's sun and increasing temperatures. As Arctic ice melts, this causes ocean levels to rise and can cause severe weather patterns all over the globe, including floods, droughts and storms that could lead to food shortages.
Deforestation: Deforestation knocks out trees which sequester atmospheric carbon dioxide in their trunks when they take it up during photosynthesis. Cutting down forests also increases albedo - the amount of reflected solar radiation coming back into space - reducing solar heat absorption by the earth's surface thus promoting excessive warming at the global level. Also, deforestation can lead to a decrease in local air quality and respiratory problems.
Farming: Each year, between 14% and 18% global anthropogenic greenhouse gases are released by the animal agriculture industry. Because of its high methane content, animal waste emits large amounts methane into the atmosphere. Reducing your intake of animal products is an effective way to lower your greenhouse gas emissions. Nitrous oxide can also be released into our atmosphere. This creates smog that harms our respiratory system.
In conclusion, while human activity has had an adverse impact on our environment for centuries, technological advances have made it possible to turn our attention towards the future. We can leverage technology through green innovation to help us move forward in our efforts to reduce climate change and keep everyone safe.
How can the world work towards a more sustainable future when faced with the challenges of climate change?
Sustainability refers to the ability to satisfy current needs while not compromising future generations' ability to do so. In light of the increasing challenges posed by climate change, there is an urgent need for drastic action to eliminate our dependence on finite resources and shift towards a more sustainable approach to how we use them.
It is crucial that we reexamine our consumption and production patterns, as well our dependence on fossil fuels, in order to move towards a sustainable future. We must seek out new technologies, renewable sources of energy, and systems that reduce harmful emissions while still meeting our everyday needs.
It is important to adopt an integrated approach to sustainability. This includes considering all aspects, such as the materials used and waste management. It also means incorporating energy utilization in transportation, industry, and industry. There are many potential solutions available including the utilization renewable energies like sun, wind, and water power; improved waste management systems; higher efficiency in agriculture; improved transport network; green building regulations; sustainable urban planning initiatives.
Furthermore, behavioral changes are required amongst individuals across different sectors throughout society for us to accomplish this goal. Education programs are necessary to help people understand the climate change issues and how they can make a positive contribution towards a more sustainable world.
Collaboration between government leaders, industry leaders, as well as citizens is the only way to make significant progress toward creating a more sustainable future for our children.
What is the effect of land use changes and deforestation on climate?
Deforestation, land use change and other factors have an immediate and direct impact on climate. Carbon dioxide, which is the most important greenhouse gas on Earth, can't be absorbed by trees if they are removed or burned. Deforestation and burning of trees for agricultural purposes removes less carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
However, land use changes can increase greenhouse gas emissions. For example, when forests are replaced with agricultural lands for livestock production, fertilizer, and pesticide use may increase emissions of nitrous oxide and methane. Clearing can also increase soils with high levels of carbon stored in them; these soils can be disturbed or turned over by farming activities and release more carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Deforestation and land-use changes can have a significant impact on regional air quality. Deforestation can lead to reduced visibility, health issues such as asthma and other respiratory problems. These changes in air quality can have a cumulative affect on global climate change. The increase in temperatures is due to more sun hitting the Earth's surfaces.
The deforestation of land and the resulting changes in land-use have made a significant contribution towards increasing global greenhouse gas emission levels. These impacts have also had a negative impact on local air quality which has further contributed to climate change. Reducing these practices should be a high priority if serious efforts toward mitigating climate change are to take place promptly.
What role do greenhouse gases play in climate change?
Greenhouse gases are a key factor in climate change. They act as an invisible shield around the Earth and trap infrared radiation, warming the atmosphere. Without them the planet would be much more colder than it currently is.
Human activity is responsible for the emission of greenhouse gases. This includes burning fossil fuels and other industries. As these activities continue to increase, more heat gets trapped in the atmosphere, leading to rising temperatures and extreme weather events.
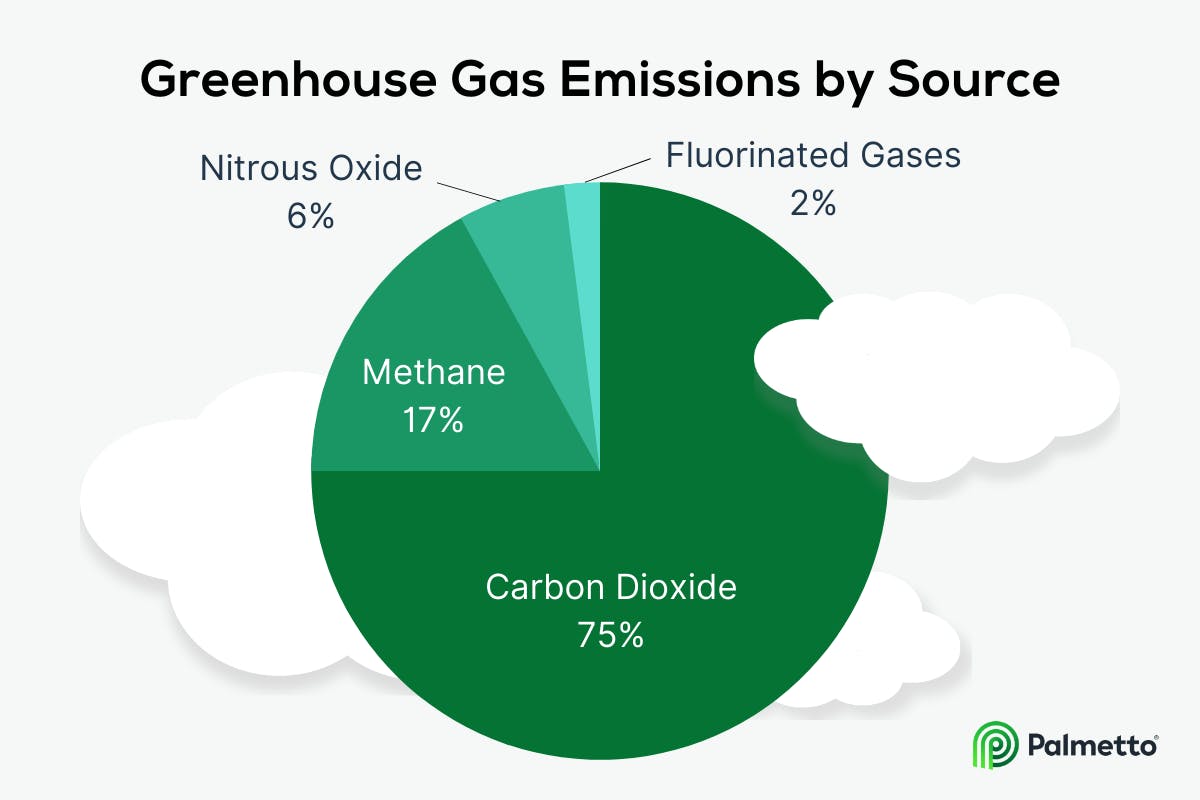
Carbon dioxide (CO2), the most potent greenhouse gas, is released by fossil fuels like gas, oil, and coal. Major contributors to climate disruption are methane (CH4) as well as nitrous dioxide (N2O) and fluorinated gases (F-gases).
Since preindustrial times, the concentration of greenhouse gases has risen significantly due to human activity. This has led worldwide warming and increased temperatures in the oceans as well as all over the planet. It is also causing major changes such as stronger storms and more droughts, melting of glaciers, rising sea levels, and increased flooding.
To avoid further damage from climate change, humans need to reduce their emissions of greenhouse gases by transitioning away from fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources like solar or wind power. We can also take measures such as reforestation or adopting agricultural methods that allow the soil to absorb more CO2 from the air. These actions will help reduce atmospheric concentrations in greenhouse gases and create a healthier ecosystem for all life.
What's the current climate in the world? And how does it change?
The current climate situation is one of uncertainty and unprecedented change. Unprecedented atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide are leading to significant temperature increases, including droughts, heat waves and changing rainfall patterns. They also cause ocean acidification, rising sea levels, and melting polarice caps.
These changes already have a profound impact upon ecosystems around the globe and are causing extinctions as well as disruption of habitats. They also threaten the livelihoods and lives of billions, especially in areas that are already suffering from resource scarcity and poverty.
Human activity has led to an increase in extreme weather events such as hurricanes, cyclones, floods, wildfires, etc. As temperatures continue their climb, this trend is expected to continue.
The effects of a rapidly changing global climate can be felt everywhere from rising food insecurity to displacement from extreme weather events or sea level rise forcing communities to relocate. Climate change is also contributing to existing social inequalities. Itdisproportionately affects marginalized communities, which lack the resources and knowledge required to adapt.
While progress has been made in some countries in terms of reducing carbon emission or developing renewable energy programs, there has yet to be any meaningful action taken at a global scale that would allow us to address these issues effectively. We must all work together now to stop further disruptions and destruction from climate change.
Statistics
- The 100 least-emitting countries generate 3 per cent of total emissions. (un.org)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
External Links
How To
How to Invest in Clean Energy, and Support the Transition to Low-Carbon Future
Clean energy is renewable energy that doesn't emit greenhouse gases or produce polluting emissions. This includes technologies like solar photovoltaic and wind power, as well as hydroelectricity, geoelectricity, and hydrogen fuel cell. Clean energy investments can provide many environmental benefits. They reduce dependence on fossil fuels and help to reduce air pollution.
Shares in companies developing innovative technologies in clean energy can be purchased by investors. This can include investing in publically traded stocks, mutual funds, and ETFs (exchange-traded funds) related to renewable energy. Investors may also be interested in direct investments in start ups or venture capital projects that fund research and technology development.
Clean energy investment is a way to support innovation and reduce harmful emissions. This investment may also lead to increased economic development by creating jobs related to the production of renewable energy systems that require skilled labor and engineers. The tax incentives programs that encourage investment into green technologies such as wind farms and solar panels can also provide investors with a financial reward.
By investing in companies focused on creating cleaner sources of electricity from renewable resources such as sun, wind, and water while avoiding activities that could harm the environment, we can support the transition to a low-carbon future while reaping economic rewards at the same time.