
The Sun is a massive ball of hot Plasma and is very close to Earth. Its energy output has decreased over the last five decades. The recent temperature spike is not caused solely by this. In the same period, greenhouse gases levels have increased dramatically. The result is that our climate has been improved by approximately 0.8 degrees Celsius.
One of the simplest explanations for this warming is the influx of carbon dioxide from the burning of fossil fuels. This gas is integral to photosynthesis in plants and breaks down when it absorbs excess heat. The plants will soon die as there is more of the noxious gas. The planet will then be dominated by microbial life.

The number of sunspots visible on the surface is a measure of solar activity. There are two 11 year cycles. During the first 11 year cycle, the sun was larger than it currently is. Over the next few centuries it will become smaller. It will eventually become a red giant. Its gravity pulls on the planet, and its orbit is affected.
The Sun also has a 22 year magnetic cycle. Interestingly, the average temperature of the lower atmosphere doesn't correlate with the solar cycle. So the answer to the question, is the sun getting hotter? Well, we don't know for sure, but we do know it is a growing beast.
Ocean currents and mountain formation are two other factors that can affect the temperature of our planet. These all are interconnected with the grand climate circle. If the climate were to shift over the next few decades, we could see an abrupt shift at the temperature.
The Earth's tidal force, which is a result of the Earth's relationship to the moon, is another factor. Tides are lower when there is a Moon between Earth, the sun and the Moon. Largely, the tides are caused by the oceans bulging towards the sun. Conversely, tides are higher when the Moon appears far away from Earth. Fortunately for humans, the latter isn't the case.
Another thing that makes the Sun the biggest and most important player in our weather is the mass of oxygen that it contains. This is vital for life on the Earth, but it can be depleted and make it difficult to live. Soon, all plants will die out, leaving only microbial life. This will make our planet uninhabitable.
The sun is not perfect because it is a main-sequence star. While some of its parts may be too small, the sun is an enormous ball of hot plasma. Its intensity has increased by around 40% since the sun's creation. It's now at the halfway point of its life.
Despite being old, it is still a significant contributor to the global climate. Even if it doesn’t get warmer over the next centuries, its outer atmosphere still has a negative impact upon Earth’s orbit.
FAQ
What does the role of greenhouse gases contribute to climate change?
Greenhouse gasses are key to climate change. They act as an invisible layer around the Earth trapping infrared radiation. This warms the atmosphere. Without them, the planet might be much colder that it is now.
Human activity is responsible for the emission of greenhouse gases. This includes burning fossil fuels and other industries. As these activities continue to increase, more heat gets trapped in the atmosphere, leading to rising temperatures and extreme weather events.
The most prevalent greenhouse gas is carbon dioxide, which is released from fossil fuels, such as oil, gas, and coal. Major contributors to climate disruption are methane (CH4) as well as nitrous dioxide (N2O) and fluorinated gases (F-gases).
Due to human activities, the concentration of greenhouse gasses has increased dramatically since preindustrial time. This has led to global warming and an increase in temperatures all over the world, as well as in our oceans. It is also leading to changes such as intense storms and droughts; melting glaciers; and rising seas.
To prevent further climate change-related damage, humanity must reduce its greenhouse gas emissions by moving away from fossil fuels and towards renewable energy sources like wind or solar power. We can also adopt reforestation methods or agricultural methods that allow the soil absorb more CO2 in the air. These activities will reduce atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations and create a healthier environment that supports all life.
What can be done to reduce or mitigate the effects of climate change?
There are many steps that can be taken in order to reduce and mitigate climate change's effects. These include reducing greenhouse emissions by using greener energy sources and better energy practices. It is important to raise awareness of climate change in order to encourage people and make them feel responsible for their actions.
What happens to developing countries when they experience the climate change effects?
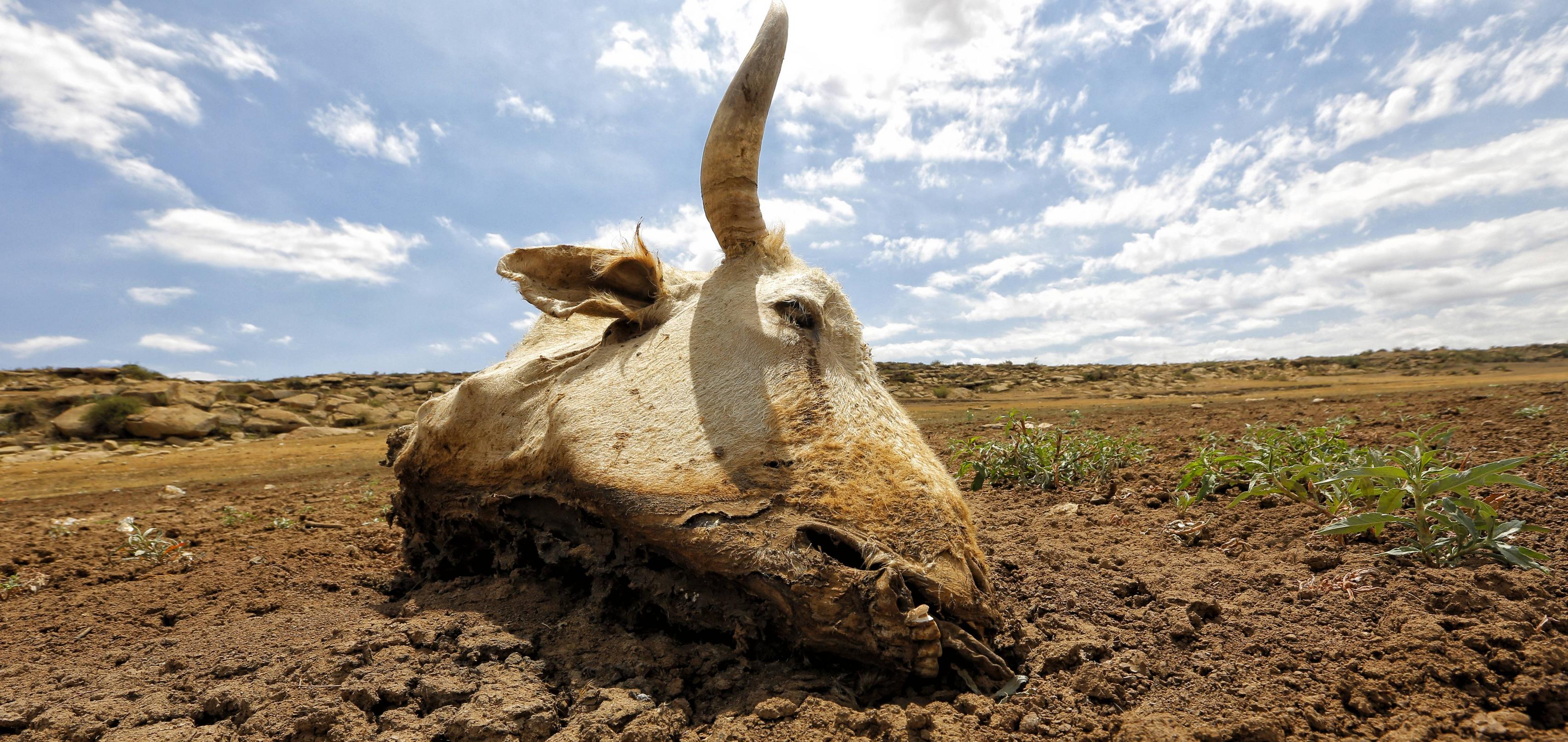
Due to their lack of access to resources, health care systems, and technology, communities and countries in developing countries are more vulnerable to climate change. Changes in temperature, precipitation, and sea levels increase pressure on already scarce resources, with floods and droughts wearing away at already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can result in a reduction in crop yields. This will be disproportionately detrimental to poorer communities who are facing food insecurity. Extreme weather events like hurricanes or heatwaves can also cause destruction to infrastructure, causing further economic inequality.
Climate change has long-term consequences. They will lead to continued resource scarcity, extreme poverty, and adverse health effects, including increased incidences of vector-borne illnesses like dengue fever and malaria. A rising sea level and extreme weather events will increase the risk of flooding, putting lives at stake in coastal areas that often lack the infrastructure or emergency services required to evacuate. These risks can be mitigated by reducing greenhouse gas emissions. However, other measures may be required such as better management of freshwater resources or easier access to healthcare facilities that aid in the prevention of diseases like malaria.
How does climate change impact marine life and oceans around the globe?
What will climate change do to the oceans and marine life of the world?
Since its inception the climate change has had an impact on the world's oceans, and the marine life within them. The depletion of the ozone layer, which causes constant oceanic warming, has caused major disruptions to marine ecosystems. This has led to coral bleaching and a decline in species.
Climate change may also be responsible for extreme sea level rises and more unpredictable weather conditions, which can prove to be fatal to coastal areas. Additionally, temperature changes may cause water systems to lose oxygen. This can result in "dead areas" in which abundant marine life is reduced.
Ocean acidification can also be caused by climate change. Excess carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere and accumulates in the oceans. Ocean acidification can raise pH levels, making it difficult for animals to adapt like crabs, clams or oysters.
The effects of higher temperatures on natural habitats can be altered by shifting their geographical locations or shrinking them all together. This could lead to certain species becoming uninhabitable. The increase in ocean stresses accelerates the already high rates of extinction worldwide. This can lead to a severe imbalance among predators and prey, which could ultimately lead to complete extinction.
Climate change has ripple effects on entire ecosystems, affecting multiple species directly and indirectly. Evaporation, lowering water volumes, or temperature shifts can all impact sustainable development of fisheries and other maritime activities. The effects of climate change continue to impact the lives of entire species on this planet.
How are extreme weather events related to climate change?
Global warming directly links extreme weather events like heat waves, floods. droughts. cyclones. storms. Global warming has caused an increase of atmospheric temperatures.
Climate scientists say that the average frequency of extreme weather-related disasters had more than doubled since 1980. The sea level rises due to rising ocean temperatures and changing wind patterns. This affects the normal distribution of storms and hurricanes in different geographical regions across the planet.
2015 El Nino brought warm water towards South America. This led to increasing temperatures at an alarming pace and heavy rains that caused floods and displacement in Peru, Bolivia and other countries. Many places, including Antarctica has recorded its highest temperature ever. This is an indication of a strong correlation between global warming trends & the occurrence/frequency of extreme weather phenomena around the globe.
Another example of climate change at work is Hurricane Irma. It was a major storm that struck Florida in 2017, causing economic losses of $50 billion.
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) concluded that human activities are increasing the severity of current climate change which naturally leads to more frequent, severe, and intense natural disasters globally hence bringing forth strong evidence regarding humans' relation to extreme weather events occurring at frequent intervals around us all.
What is climate Change and how does this happen?
Climate change refers back to the long-term shifts occurring in global weather patterns as a result of an increase in greenhouse gases. These gases trap heat, leading to global temperature rises that can result in a range of climate and weather changes. This could lead to rising sea levels, melting glaciers and extreme storms and dry spells, widespread coral reef bleaching, and the extinction of species.
Climate change is primarily caused by human activity, such as the burning of fossil fuels for electricity, transportation, and cutting down forests. This is because these activities release huge amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. It warms the planet faster than natural processes like volcano eruptions.
Another major contributor to the global greenhouse gas emission is deforestation. It accounts for around 15-20%. When trees are cut down or burned it releases their stored carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere. Forests also act as a natural carbon sink, removing CO2 from the atmosphere; without this absorption capacity, carbon dioxide levels around the globe will continue to rise, with disastrous consequences for ecosystems.
Not only does CO2 release into the atmosphere but it also releases other harmful gasses, such as methane(CH4) and nitrogen oxide (N2O). Methane has been used extensively in industrial processes and contributes significantly to atmospheric warming while N2O is emitted primarily from agricultural soil management activities like fertilization or tilling which release excess levels of nitrogen into soil leading to N2O production upon microbial contact.
Humanity must work together across all levels of society, economy, and politics to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. We need to shift from dependence on fossil fuels and towards renewable energy sources like solar, wind, and low-carbon hydrogen fuels in order to limit climate change. Smart solutions that encourage zero-waste living and replace polluting fossil fuels could help reduce atmospheric pollution and heat buildup. We can take responsibility for how we impact the environment and begin to mitigate it. Preservation measures such as reforestation help preserve biodiversity while also absorbing large amounts of harmful CO2 back into the natural world. This is a powerful way to address climate change and restore balance for future generations.
Statistics
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to make your home more energy-efficient and combat climate change
Your home's energy efficiency is one of the most cost-effective ways to cut your carbon footprint, lower your utility bills, and improve your quality of life.
First, ensure your home has proper insulation and sealing. Make sure windows and doors are correctly fitted, look for drafts around pipes and vents, add weather stripping where necessary, and fill any gaps around window frames or door frames with caulking.
Insulate your floors, ceilings, & walls for maximum energy efficiency. You should inspect your attic and other areas for leaks.
Lighting can account up to 18% for household electricity consumption. Switch to LED light bulbs to save up to 80 percent over traditional incandescent bulbs. Installing motion sensors and timers will also help you save additional money by turning off lights as needed.
Replacing an old boiler or furnace can dramatically reduce energy bills as newer models are much more efficient. A programmable thermostat allows you to control the temperature based on who is home and who is away.
Switch out all old windows with new double-glazed ones which provide better insulation and don't allow heat to escape through them. Low-flow showerheads are a great option, as they reduce water consumption but maintain adequate pressure.
ENERGY STAR rated appliances are more efficient than non-certified models and can use as much as 50% less power. Make sure to take care of the little details, such as unplugging TV boxes and phone chargers when not in use. This could help save you significant energy.
These are just a few of the steps that can dramatically reduce your impact on climate change and lower monthly electricity bills, making it easier to live at home.