
There is a lot to be uncertain about the economics of climate changes. Among other things, the impacts of climate change are hard to quantify in monetary terms. It is difficult for us to estimate the amount of damage that will occur and how long it takes to solve the problem. We also don't know what the benefits of adaptation or mitigation are. This uncertainty is magnified when the issue is global.
A temperature rise of 3oC is the most common estimate of the impacts of increasing atmospheric carbon dioxide emission by doubling it. This would translate into a global cost of 0.5% GDP per year by the mid-century. This number may be lower. It is possible that the cost of a fully functioning economy would be even lower.
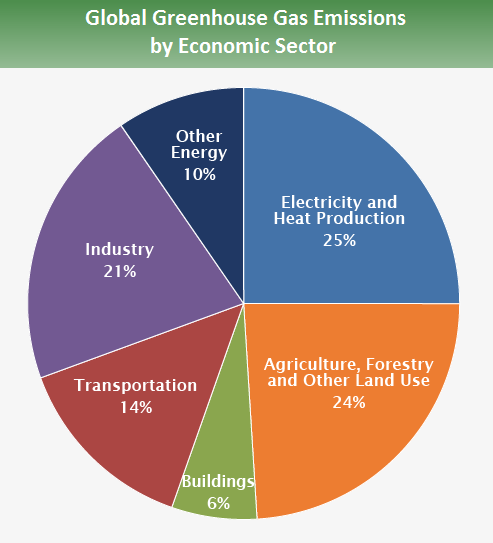
Integrated assessment methods (IAMs), are a type model that can account for the costs of multiple scenarios. These models can be used in order to assess the potential impact of a given policy. IAMs account for a variety factors, such economic growth and technological advancement. They also consider demographics and changes in the environment. An integrated model allows for the evaluation of the financial effects of climate policy.
Among other things, a discount rate can be used to capture the social cost of carbon. This allows for the cost of future actions to be compared against inaction. A discount rate may not give sufficient weight to future events, depending on the case. The value of future consumption could be affected by time, nature and who gets it. The discount rate might not reflect catastrophic events such as a collapse of society.
Economists are weighing the pros and cons of discounting the future's value because of this uncertainty. They have also noted the importance of accounting for high impact, low probability outcomes. But, the benefits associated with achieving a goal are often greater than those of inaction.
Although there are uncertainties surrounding the impact of climate change, the benefits of reducing greenhouse gas emissions are clear. There are many methods to reduce GHG emission, but technological innovations that make it possible to shift to a lower-carbon economy are the best. In 2026, renewable power capacities are expected to grow 60% compared to 2020 levels. Energy from renewable sources is currently more affordable than energy generated using fossil fuels.

Climate change is one of the largest challenges in the world. Many countries have set goals for net carbon neutrality in 2050. This goal would require significant structural changes to the economy and capital market. Nevertheless, the costs of achieving this goal are less than 0.5% of GDP by mid-century.
As a matter of fact, avoiding climate change is technically feasible. However, there are still many uncertainties and technological innovation at a slow pace. Economic growth is unpredictable.
To address these uncertainties the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change(IPCC), reported that limiting the warming to 1.5 degree Celsius by 2060 was the most prudent option. Despite the risk, the international community has committed the 1.5 degree target. The target has been accepted by the majority of national governments.
FAQ
What can we do to help the climate change process?
Climate change can be attributed to human activity. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change(IPCC) states that humans are responsible more than 70% for global warming in the past 20 years.
Burning fossil Fuels: The atmosphere is effected by the combustion of fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas. This adds to already existing levels of atmospheric CO2, which act as a "greenhouse gas" by trapping heat from the sun in Earth's atmosphere and increasing temperatures even further. This can result in an increase in ocean levels due to Arctic ice melting. This creates unpredictable weather patterns that can disrupt food production and threaten human health.
Deforestation: Deforestation knocks out trees which sequester atmospheric carbon dioxide in their trunks when they take it up during photosynthesis. Cutting down forests also increases albedo - the amount of reflected solar radiation coming back into space - reducing solar heat absorption by the earth's surface thus promoting excessive warming at the global level. As well decreases local air quality with deforestation being linked permanently with respiratory issues.
Farming: Each year, between 14% and 18% global anthropogenic greenhouse gases are released by the animal agriculture industry. Large amounts of methane gas are released by animal waste due to its richness in methane bacteria. Eating less or none of these products can reduce global warming.
Conclusion: While human activity has had a significant impact on the environment over centuries, technology advancements such as renewable energy sources have allowed us to look towards the future. The results of these industries, which emit carbon, will soon be clear when we use technology through green innovations to make it eco-friendly and reduce climate change. All people are safe in a healthy, prosperous natural world.
What impact does climate change have on biodiversity and ecosystems
Climate change is having a wide range of effects on biodiversity as well as ecosystems. Rising temperatures, changes in extreme weather events and sea levels, as well as increased acidity in the ocean are just some of the issues affecting wildlife and ecosystems today.
These changes can result in shifts of habitat areas, disrupting food chains or affecting population numbers or distributions. With potentially devastating consequences for biodiversity, ecosystems and their functioning, these shifts in climate conditions could cause significant impacts. Changes in the hydrological cycles can also have an impact on water availability for species that live in aquatic environments.
Climate change can also lead to rising temperatures and more extremes, such as droughts or floods. This places more strain on already fragile systems like coral reefs, tropical rainforests, and other ecosystems. Up to 30% of all animal species could be extinct by 2050 due to climate change, which would lead to further losses in ecological communities.
Climate change is an enormous threat to biodiversity and to human societies which depend on functioning ecosystems. The best way to minimize its impact is to work at every level to reduce global warming trends. Future damages can be avoided with prudent management practices.
How does the politics of climate change impact global efforts to address it?
Climate change is a highly politicized issue that has created a great deal of division among nations, governments, and individuals. The implementation of measures to address climate change is affected by the political stances of various actors. It has been difficult for global consensus to address this urgent environment crisis.
Scientific consensus is unanimous that human-caused climate change is real and needs to be addressed. The politics surrounding these issues often undermines global cooperation which is needed to make effective progress in implementing sustainable energy practices, upholding regulations protecting natural habitats, researching viable technological solutions, and other climate change interventions.
In particular, various governments around the world are keen to protect their economic interests and enforce measures that would limit business activities as little as possible; this frequently conflicts with the regulations that experts recommend for addressing climate change in an efficient manner. It is very difficult for any one state or group of countries to effectively address climate change without strong commitments from all participants and broad-scale international action.
The difficulty of reaching a full consensus about the best way to combat climate change is further complicated by differences in power dynamics. Countries with more economic power often appoint their own representatives to represent them on international bodies responsible for negotiations over the environment - this can lead to lopsided discussions of those countries' perceived interests versus the collective interest of all involved parties. In addition, potential side effects from implementing radical changes such as geoengineering have been debated heavily at both national and international levels.
Also at the grassroots level, grassroots movements have fought against powerful opponents such as corporate ownerships. These lobbies are trying to preserve politically favorable positions for their industry especially when it is about funding research into alternative sources of energy production or enforcing Renewable Energy Technology mandates. If individual governments want to make valid progress in the subject matter themselves instead of seeking short-term benefits or spectacles, they must be clearheaded about possible outcomes.
It is essential to distribute resources properly to any intervention program, and to be mindful of political divisions within nations, if we want to see an effective coordinated effort to mitigate our current environmental crisis.
How are developing countries and communities affected by climate change?
Because of their limited access and lack of technology and healthcare, the impact climate change has on developing countries and communities is particularly severe. Temperature, precipitation, sea levels, and rainfall changes put additional pressure on already scarce resources. Additionally, floods and droughts cause havoc in already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can cause decreased crop yields. This will have a significant impact on poorer communities suffering from food insecurity. Extreme weather events like hurricanes or heatwaves can also cause destruction to infrastructure, causing further economic inequality.
Climate change has long-term consequences. They will lead to continued resource scarcity, extreme poverty, and adverse health effects, including increased incidences of vector-borne illnesses like dengue fever and malaria. In addition, there will be a higher risk of flooding due to rising sea levels coupled with extreme weather events putting lives at risk in coastal areas where populations often lack the adequate infrastructure or emergency services needed for evacuation. Building resilience against these risks necessarily involves mitigating greenhouse gas emissions but may require other measures such as improved management of freshwater resources and better access to health facilities which assists with prevention strategies for diseases like malaria.
What is the current state of the global climate and how is it changing?
The current climate is characterized by unprecedented uncertainty and change. Unprecedented atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide are leading to significant temperature increases, including droughts, heat waves and changing rainfall patterns. They also cause ocean acidification, rising sea levels, and melting polarice caps.
These changes already have a profound impact upon ecosystems around the globe and are causing extinctions as well as disruption of habitats. They are also threatening lives and livelihoods for billions of people, especially those who live in areas with resource scarcity.
Increased average surface temperatures, which are caused by human activity, have led to an increase of extreme weather events, such as hurricanes or cyclones. As temperatures continue their climb, this trend is expected to continue.
The effects of a rapidly changing global climate can be felt everywhere from rising food insecurity to displacement from extreme weather events or sea level rise forcing communities to relocate. Climate change is also increasing social inequality bydisproportionately impacting marginalized communities who lack the necessary resources and knowledge to adapt.
There has been progress in some areas, such as the reduction of carbon emissions or initiatives for renewable energy in certain countries. However, there is no global initiative that can be taken to effectively mitigate these changes. To prevent further destruction and devastation caused by climate change, all countries must work together to take immediate action and plan for adaptation in an ever-changing world.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Invest Clean Energy to Support a Low-Carbon Transition
Clean energy is a form of renewable energy that does not produce pollution or emit carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases. It includes technologies such a solar photovoltaic (Solar Photovoltaic), wind power, hydroelectricity and geothermal energy. Clean energy sources offer many environmental benefits. These include a reduction in dependence on fossil fuels, reduced air pollution from traditional electricity methods, and more reliable access to remote areas.
By purchasing shares in companies that are developing new technologies in the sector, investors can become involved in clean energy projects. This could be done by investing in publically traded stock, mutual funds, or ETFs related to renewable energies. Investors might also consider direct investments in start-ups or venture funds to finance research and development for clean technology technologies.
Investors in clean energy support innovation that reduces the harmful effects of traditional sources of electricity generation. This investment can also help increase economic development through the creation of jobs in the production and engineering of renewable energy systems. Lastly, investing in clean energy can bring investors a financial return through tax incentives programs that encourage investments into green technologies, such as wind farms, solar panels, or biomass heat generation systems.
We can both support the transition from low-carbon to a low carbon future by investing in companies that are focused on producing electricity from renewable resources like sun, wind, water and avoid activities that may harm the environment.