Adaptation to climate change involves changes to the natural environment and social structures in order to reduce risk from the harmful effects of climate change. Adaptation is possible at the local, regional, and global levels. It involves both institutional and structural approaches as well as early warning systems for natural catastrophes. The potential benefits of climate changes can also be used to adapt.
The impacts of climate change are felt on a variety of levels, including the weather, sea level, and water resources. These changes are likely to lead to more severe extreme weather events. These changes can also impact the availability of water throughout the year. This can lead to flooding and more frequent droughts. In some areas, the warming will lead to longer growing seasons. It can be difficult to adapt to changing conditions at higher levels when the climate is changing faster.

Many adaptation solutions are possible, including rebuilding flood defenses or redesigning business operations. Adaptation actions can help strengthen livelihoods and rebuild nature. They also increase innovation. California has a town that uses goats in clearing vegetation from its streets. A similar project in Papua New Guinea helped people cope better with storms.
Adaptation can be an iterative process. As more information becomes available about climate change's effects, adaptation will become more efficient. Successful adaptation relies on continued engagement from stakeholders. It must also take into account vulnerable groups.
Many species and ecosystems have reached hard adaptation limits. It means they are unable or unwilling to adapt to changing environmental conditions. These limits are caused primarily by cultural, social and financial barriers. Many countries are working to adapt their climate strategies.
Countries with higher adaptive capacity and development are better able to adapt to climate change. Nonetheless, some societies lack the capacity to adapt successfully, especially those that are low-income. The adaptive capacity of those who have established strong social institutions is also higher. However, these characteristics are not necessarily associated with higher equity or well being.

Adaptation plays a critical role in helping communities adapt to and deal with the inevitable changes that will occur. For example, the coast may require new sea walls or restoration of wetlands. Also, cities are using community energy planning and better draining streets.
Despite the progress, many nations are still lacking in the ability to adequately address the effects of climate change. It is difficult to find the resources needed to build storm-resistant infrastructure, and sea walls, particularly in low-income areas. It is also difficult to find funding for adaptation measures, such as in aquaculture, fishing, and forestry.
Adaptation can be a critical step in reducing climate change's impact. It can offer multiple benefits like reducing food insecurity or increasing the productivity of fish stocks. Climate adaptation investing can also help reduce future costs.
FAQ
How does climate politics affect global efforts for its resolution?
Climate change has become a highly politicized topic that has caused great divisions among governments, nations, and individuals. Politics of different actors can have an impact on the implementation of climate change measures. It is becoming difficult to reach consensus on global efforts for addressing this urgent environmental crisis.
The overwhelming majority of scientists agree with the fact that human-generated global warming is real. It is urgent for action to address it. These politics often hamper global cooperation needed to achieve effective progress in implementing sustainable energy practices.
Many governments around the globe want to protect business interests and enforce policies that restrict business activities. This often clashes with regulations that experts recommend for effectively addressing climate change. Without strong commitments from all participating countries and wide-scale international action, it becomes very difficult for any single state or group of states to adequately address climate change through legislation or otherwise.
It is difficult to reach a consensus about how to address climate change because of differences in power dynamics between countries. The countries with greater economic power tend to nominate their own representatives to represent them in international bodies that are responsible for the environment. This can lead to biased discussions between the perceived interests of the country and the collective interest of all parties. At both the national and international level, there have been extensive discussions about potential side effects of radical changes like geoengineering.
A grassroots movement has also struggled against powerful opposition, including corporate ownerships as well-funded lobbyists trying to keep their industries politically favorable. This is especially true when it comes funding research into alternative energy production and enforcing mandates for renewable energy technology. Individual governments need to be clear about the potential rewards and outcomes of making valid progress on the issue. They cannot seek short-term spectacles or gains to gain public support.
Properly distributing resources allocated towards any intervention program while being mindful of political divisions between nations will be critical if any coordinated effort aimed at mitigating our current environmental crisis is going successfully to come to fruition.
What are the impacts of climate change on developing countries and communities?
Due to their limited access to healthcare and technology, developing countries and communities are especially vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. Climate change can increase the pressure on already limited resources. Floods and droughts can also cause damage to already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can cause a drop in crop yields which will adversely impact the poorer communities that are struggling to feed their families. Moreover, extreme weather events such as heatwaves and hurricanes can result in the destruction of infrastructure and displacement of people, further perpetuating economic inequality.
Climate change will have long-term effects on resources, poverty, and health. This includes an increase in the number of vector-borne disease such as dengue fever or malaria. A rise in sea levels and extreme weather events will lead to increased flooding. This could put lives at risk in coastal regions, where there is often a lack of emergency services or infrastructure. While mitigating greenhouse gases is essential to build resilience to these risks, there are other options available. These include better management of freshwater resources and easier access for health facilities. This helps with the prevention of diseases such as malaria.
What is the climate impact of land use and deforestation?
Deforestation and land use change have a direct and immediate impact on the climate. The trees that have been cut down or burned can no longer absorb carbon dioxide, one of Earth's most important greenhouse gases. Therefore, when trees are cleared by deforestation or burned for agricultural purposes, less carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere.
However, land use changes can increase greenhouse gas emissions. In addition to methane and nitrous oxide, pesticide and fertilizer use can increase when forests are converted into agricultural lands. Additionally, clearing soils rich in carbon can increase the exposure; soils that are disturbed by farming activities or turned over can release more carbon dioxide into our atmosphere.
Deforestation and land-use changes can have a significant impact on regional air quality. Deforestation can lead to reduced visibility, health issues such as asthma and other respiratory problems. The cumulative effects of these changes in local air quality could have an impact on global climate change. Higher temperatures can be caused by more sunlight reaching the Earth's surface due to lower aerosol particles.
In conclusion, both deforestation (and land-use) change have been a major contributor to rising levels of global greenhouse gases emissions. Additionally, they have had negative effects on local airquality that has contributed further to climate changes. If serious efforts towards mitigating climate changes are to be made quickly, then reducing these practices must be a priority.
What is the effect of climate change upon biodiversity and ecosystems?
Climate change can have a variety of impacts on biodiversity, ecosystems, and the environment. The most pressing issues facing wildlife and ecosystems are rising temperatures, extreme weather events, sea level rise, and increased acidity.
These changes can result in shifts of habitat areas, disrupting food chains or affecting population numbers or distributions. With potentially devastating consequences for biodiversity, ecosystems and their functioning, these shifts in climate conditions could cause significant impacts. Water availability can be affected by changes in hydrological cycles.
Climate changes can lead to higher temperatures and more frequent extremes (such as droughts) which put more stress on already fragile systems, like coral reefs or tropical forests. Climate change could lead to the extermination of up to 30% of animal species by 2050. This would cause further ecological community losses.
Climate change is an enormous threat to biodiversity and to human societies which depend on functioning ecosystems. At all levels, efforts should be made to decrease global warming trends. Future damage should be avoided if possible through careful management.
What is the role of greenhouse gases in climate change?
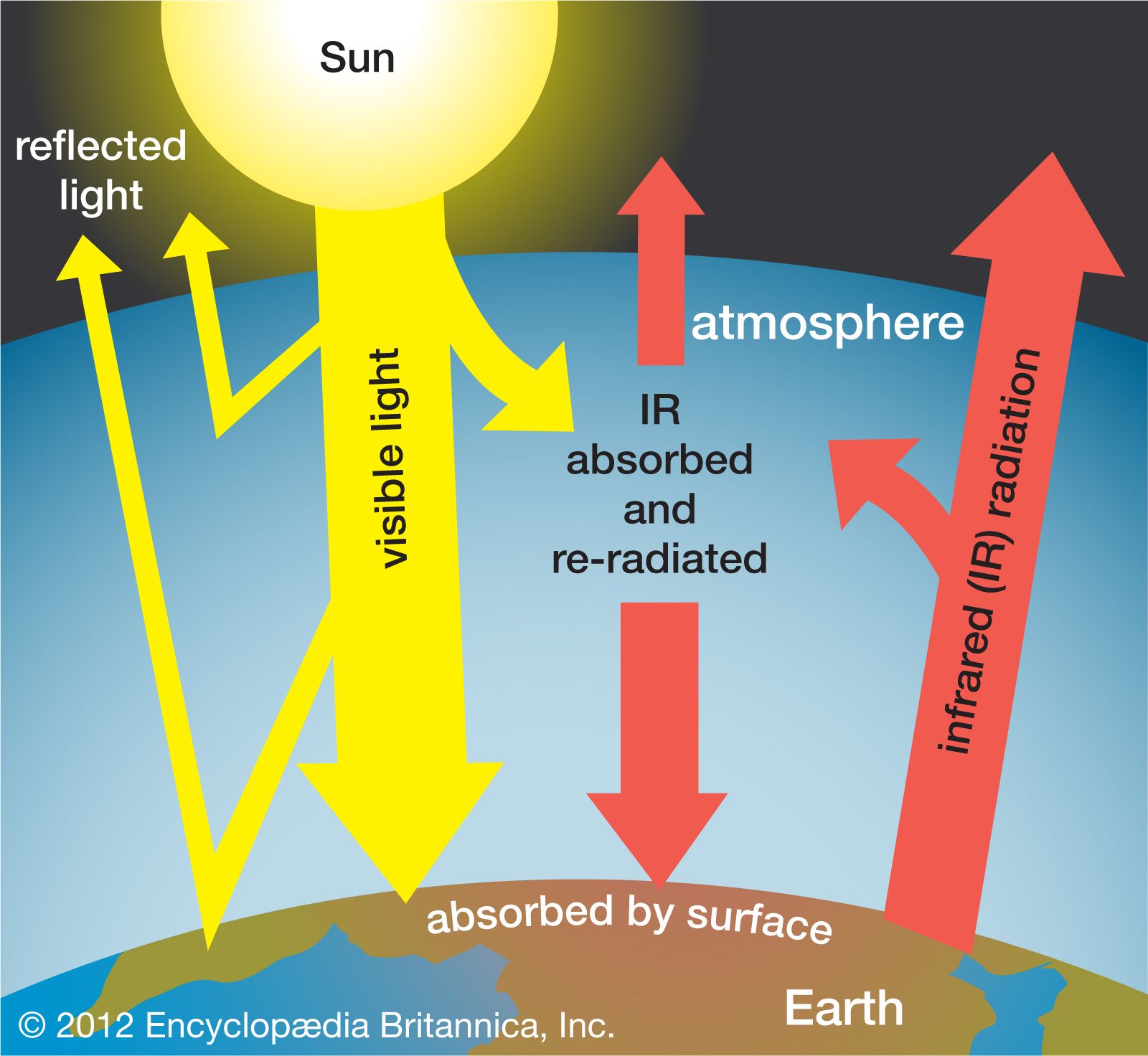
Greenhouse gases are a key factor in climate change. They act as an invisible shield around the Earth and trap infrared radiation, warming the atmosphere. Without them, the Earth would be much colder today than it is today.
Human activity can cause greenhouse gases, such as the burning of fossil fuels and other industries that emit emissions. These activities will continue to increase heat trapping in the atmosphere. This will lead to increasing temperatures and extreme weather conditions.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most common greenhouse gas. It is produced when fossil fuels like coal, oil and gas are burned. Major contributors to climate disruption are methane (CH4) as well as nitrous dioxide (N2O) and fluorinated gases (F-gases).
Since preindustrial times, the concentration of greenhouse gases has risen significantly due to human activity. Global warming has resulted in an increase of temperatures around the world and in our oceans. It's also causing changes like more severe storms and droughts as well as melting glaciers and rising sea level.
To avoid more damage from climate changes, humans must reduce their emissions by switching away from fossil energy to increase their use of renewable energy like solar and wind power. You can also reduce greenhouse gas emissions by reforestation and adopting farming methods that allow soil to absorb more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. These activities will reduce atmospheric greenhouse gas concentrations and create a healthier environment that supports all life.
Statistics
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Indigenous peoples and local communities receive less than 1% of all climate funding despite scoring wins for people and nature Africa's broken food markets must be fixed to tackle hunger (climatechangenews.com)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
External Links
How To
How to Invest Clean Energy and Support a Transition to a Low Carbon Future
Clean energy is a form of renewable energy that does not produce pollution or emit carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases. It can include technologies such as solar photovoltaics, wind power and hydroelectricity. Clean energy investments can provide many environmental benefits. They reduce dependence on fossil fuels and help to reduce air pollution.
By purchasing shares in companies that are developing new technologies in the sector, investors can become involved in clean energy projects. This includes investing directly in stocks, mutual funds, ETFs, and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) related to clean energy. Investors might also consider direct investments in start-ups or venture funds to finance research and development for clean technology technologies.
Clean energy investment is a way to support innovation and reduce harmful emissions. This investment could lead to greater economic development as it may create jobs in the field of producing renewable energy systems, which require engineers and skilled labor. Through tax incentives programs, investors can get a financial return by investing in clean energy technologies such as solar panels and wind farms.
By investing in companies focused on creating cleaner sources of electricity from renewable resources such as sun, wind, and water while avoiding activities that could harm the environment, we can support the transition to a low-carbon future while reaping economic rewards at the same time.