
Although the connection between climate change, national security and national security is not new in recent years, it has received increasing public attention. This is because climate change's human effects can exacerbate existing threats and increase the likelihood of non-violent conflict. These threats can affect everything from economic stability to the health of nations.
National security is not the only concern of climate change, but it has been a topic of constant discussion in national security policy guidelines since 1991. These issues include increased heat waves, drought, flooding, and sea level rise. For example, the Air Force chief of staff has cited conflict in Syria as an example of the impact of climate change.
Loss of agricultural production is one major consequence of climate change. In tropical areas, crops are unable to withstand the heat and dry conditions. Crop yields could drop by 20-50% in the next few decades. This will increase food insecurity and hunger. Additionally, more frequent and severe weather events can result in business interruptions or property damage. This can also increase the need for humanitarian assistance.
Adaptation strategies are essential to combat the threat from climate change. The United States has faced a difficult task convincing other countries about the need to address global warming. Wealthy nations will have to step up and cut emissions in ways that go beyond the current promises. The most affected will be developing countries.
The Center for a New American Security Military Advisory Board (CNA), has published a new report identifying the effects of climate changes on national security. According to the report a changing climate could significantly increase the probability of civil disorder and armed conflicts in volatile areas around the globe. These include areas where climate change will cause disruptions to social order, lower access for basic necessities, and weaken fragile governments.
The report cites the example of a region in Africa that could experience a reduction in access to water and food, causing more frequent, more severe, and more expensive disasters. Meanwhile, a more frequent and pronounced heat wave will increase the risks of infectious diseases. Climate change will also have a negative impact on the Arctic Ocean and increase competition for resources. Global warming is predicted to result in tens or millions of people being forced from their homes by 2050.
These and other future threats are the responsibility of the military. In this context, the overemphasis on the climate change as a national security threat risks underappreciating the interdisciplinary nature of successful adaptation solutions. It is better to concentrate on international assistance than military solutions.
Nearly 60 percent of Americans see climate change as a major threat to their country, according to the Center for Disease Control. Although Republicans tend believe that climate change is caused principally by human activity, Democrats are more likely than Republicans to blame local factors.
FAQ
How can the planet move toward a more sustainable world in the face of climate change-related challenges?
Sustainability means being able to provide for current needs and not compromise future generations' ability. We must take urgent action to reduce our dependency on finite resources and adopt a more sustainable way of using them.
For a more sustainable future it is essential to rethink our current consumption and production models, as we also need to reduce our dependence upon natural resources such fossil fuels. We must find new technologies, renewable resources of energy and systems that reduce harmful emissions while still meeting our daily needs.
Furthermore, it is crucial to take a holistic approach to sustainability. This includes considering all aspects, such as the materials used and waste management. It also means incorporating energy utilization in transportation, industry, and industry. There are many options available, including the use of renewable energies like solar, wind and hydropower, improved waste management systems, increased efficiency in agriculture, improved transport networks, green building regulations, and sustainable urban planning.
We need behavioral changes to reach this goal across society. Education programs will be needed to support individuals in understanding climate change and how they can positively contribute towards a sustainable world.
Collaboration between government leaders, industry leaders, as well as citizens is the only way to make significant progress toward creating a more sustainable future for our children.
How do climate change and global warming impact agriculture and food security?
Global warming and climate change have an immediate impact on agriculture and food safety. The changing climate can affect rainfall patterns, temperatures, soil moisture levels, and extreme weather. This can affect farming activities and reduce crop yields. It can also lead to a decrease in agricultural biodiversity. Warmer temperatures can cause crop diseases and pests to multiply. It can also affect the ranges that are suitable for agricultural production. This can result in higher costs for food production, and worsening hunger and nutrition around the world.
Rising sea levels pose an additional threat, as they could inundate important agricultural land in many coastal regions, leading to increased salinity levels in wetlands where important crops are grown. Livestock production is similarly affected by the changing climate - high temperatures during summer months can reduce fertility rates for animals like cattle, sheep, and goats, resulting in lower milk yields which exacerbate food insecurity across communities.
Global warming and climate change are complex issues. However, governments around the world are making efforts to reduce these effects through adaptation strategies such as climate-smart agricultural (CSA) strategic investments. This involves encouraging sustainable methods, such a crop rotation technique or the conservation of indigenous seed varieties. This helps to mitigate adverse effects from changing weather or other environmental stressors. In addition, CSA strategies call for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions through the use of renewable energy sources and the reduction of deforestation-related logging activities.
In order to ensure food safety in an ever-changing environment, farmers across the globe will need to use technologies that are more sensitive and adaptable to changing climates. Infrastructure must be improved so that the necessary actions can be taken when critical crop thresholds have been reached. This includes creating stable irrigation networks with adequate water supply at times when water is scarce or when temperatures rise. For sustainable solutions to be created that will ensure the continued compliance with international dietary guidelines in our ever-changing climates, it is necessary to have a cohesive collaboration among all stakeholders. This includes government officials at international levels as well as NGOs located at local communities.
What does climate change politics have to do with global efforts to combat it?
Climate change is highly politicized and has caused division between governments, individuals, and nations. Politicians of many actors influence the implementation of actions to address climate change. It has become increasingly difficult to come to an agreement on how to address this urgent environmental crisis globally.
The vast majority of scientific opinion agrees that human-generated climate change is real and requires urgent action. The politics surrounding these issues often undermines global cooperation which is needed to make effective progress in implementing sustainable energy practices, upholding regulations protecting natural habitats, researching viable technological solutions, and other climate change interventions.
Many governments across the globe are determined to protect their own economic interests and enforce regulations that restrict business activities. This frequently clashes with the regulations that experts recommend in order to tackle climate change effectively. Without strong commitments of all participating countries, and international action on a large scale, it becomes difficult for any state or group or states to effectively address climate-change legislation.
Different power dynamics can make it difficult to achieve full consensus on the best ways to address climate change. Countries with greater economic power are more likely to elect their own representatives to the international bodies responsible for negotiations on the environment. This can cause lopsided discussions about the interests of each country versus the collective interest all parties. A number of potential side effects that could be caused by radical changes like geoengineering were also discussed at national and international levels.
At a grassroots level too, grassroots movements have struggled against powerful opponents including corporate ownerships and well-funded lobbies trying to maintain politically favorable positions for their industries especially when it comes to funding research into alternative forms of energy production or enforcing renewable energy technology mandates such as low emissions targets for vehicles etcetera - meaning individual governments must remain clearheaded about potential rewards and outcomes if they are going actively try to make valid progress on the matter in the question itself instead seeking public favor through short-term gains or even spectacles.
A coordinated effort to reduce our environmental crisis will only succeed if resources are distributed properly and there is no political divide between nations.
What role does the energy sector play in climate change? How can this be addressed?
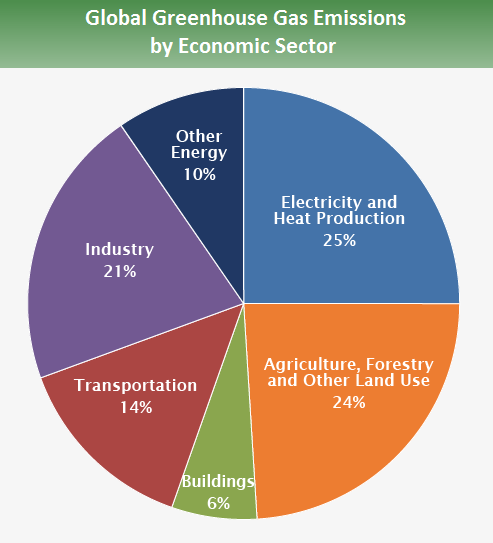
It is crucial that the energy sector plays a significant role in climate change. Global warming is caused by the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. This traps heat and causes an increase in Earth's average temperature.
This is why energy sources need to shift away from carbon-emitting resources like coal and natural gas and instead switch towards renewable energy sources such as solar, wind and geothermal. This shift can be made possible by both government policy and incentives as well investments in innovative technology like hydrogen-fuel cells. Businesses and households will be able to reduce their carbon emissions and lower their electricity bills if they invest in infrastructure that supports renewable sources.
Other methods include transitioning away from polluting transportation options like petroleum-fueled cars and moving towards electric vehicles or public transport. The government has great power to help societies transition away from oil-based infrastructures. They can support research into battery technology and encourage consumers to invest in cleaner modes.
Companies must also adopt green business practices to reduce their carbon footprint. This includes installing better insulation in offices and implementing energy efficiency plans at production plants. This can dramatically reduce operational costs, while improving environmental performance metrics.
These initiatives should be championed at all levels, not just at company level but also at government. Raising taxes on pollution products encourages individuals and businesses to stop using harmful practices. While this may be a financial outlay for polluters, providing vouchers for or subsidy for low-carbon products can create a continuing market to support sustainability efforts. It is important to recognize that tackling climate change takes a lot of effort from both the private and public sectors.
What are the impacts of climate change on developing countries and communities?
Due to their limited access to healthcare and technology, developing countries and communities are especially vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. Temperature, precipitation, sea levels, and rainfall changes put additional pressure on already scarce resources. Additionally, floods and droughts cause havoc in already fragile ecosystems. Rising temperatures can cause a drop in crop yields which will adversely impact the poorer communities that are struggling to feed their families. Moreover, extreme weather events such as heatwaves and hurricanes can result in the destruction of infrastructure and displacement of people, further perpetuating economic inequality.
Climate change will have long-term effects on resources, poverty, and health. This includes an increase in the number of vector-borne disease such as dengue fever or malaria. A rising sea level and extreme weather events will increase the risk of flooding, putting lives at stake in coastal areas that often lack the infrastructure or emergency services required to evacuate. While mitigating greenhouse gases is essential to build resilience to these risks, there are other options available. These include better management of freshwater resources and easier access for health facilities. This helps with the prevention of diseases such as malaria.
What is the effect of land use changes and deforestation on climate?
Climate change is directly affected by land use changes and deforestation. If trees are cut down, or burned, carbon dioxide, one the most important greenhouse gases, is no longer absorbed. Therefore, when trees are cleared by deforestation or burned for agricultural purposes, less carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere.
At the same time, changes in land use can also release more greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. For example, when forests are replaced with agricultural lands for livestock production, fertilizer, and pesticide use may increase emissions of nitrous oxide and methane. Clearance can increase exposure of soils that have large amounts stored carbon. These soils release carbon dioxide when they are turned over or disturbed through farming activities.
The impacts of deforestation and land-use change extend beyond just increased greenhouse gas emissions; it can also have an impact on regional air quality. The smoke from deforestation's burning events has been linked to poor visibility and other health concerns, such as asthma or other respiratory diseases. Because of the reduced amount of aerosol particles in our atmosphere, which scatter sunlight off the Earth's surface, these changes can have a cumulative impact on global climate.
In conclusion, both deforestation (and land-use) change have been a major contributor to rising levels of global greenhouse gases emissions. Additionally, they have had negative effects on local airquality that has contributed further to climate changes. If serious efforts to mitigate climate change are to be made, it is important that these practices are reduced.
Statistics
- According to the 2014 report on Climate Change Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability (page 8) from the United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, governments at various levels are also getting better at adaptation. (climate.nasa.gov)
- Fossil fuel production must decline by roughly 6 percent per year between 2020 and 2030. (un.org)
- features Earth's average surface temperature in 2022 tied with 2015 as the fifth warmest on record, according to an analysis by NASA. (climate.nasa.gov)
- This source accounts for about 10% of all the water that enters this highly productive farmland, including rivers and rain. (climate.nasa.gov)
- The 10 countries with the largest emissions contribute 68 percent. (un.org)
External Links
How To
How to Support Climate-Friendly Policies and Companies
Individuals can take several actions to support climate friendly policies and companies. This can include speaking out against non-climate-friendly businesses or politicians, voting for pro-environment candidates, writing letters or emails of encouragement to those who are already taking positive action towards the environment, and signing petitions in favor of policies that encourage and support climate-friendliness. Individuals can take practical steps like switching to greener providers or choosing more sustainable products than those that emit higher carbon emissions.
A key step to supporting climate-friendly policies is reducing one's carbon footprint. This can involve changing simple daily habits such as unplugging appliances or switching off lights when not needed, commuting via public transportation or carpooling instead of driving alone, using eco-friendly household items like biodegradable cleaning supplies and composting kitchen scraps rather than adding them to landfills, wearing clothes made from sustainable fibers often grown without chemicals, choosing locally sourced food whenever possible, setting up energy-efficient energy systems at home using solar panels or wind turbines, and planting trees around your property which absorb CO2 (carbon dioxide) from the atmosphere.
Investors who are keen to support climate-friendly policies will want to find companies that produce lower carbon emissions before investing. Additionally, they should look into their portfolios periodically to ensure they meet the sustainability standards they have set themselves ahead of time. Green bond investors may be concerned that they do not invest in activities that emit more greenhouse gases than they take out. Investors should look out for opportunities to use funds towards green business activities. This includes renewable energy alternatives, community-building projects, and initiatives that promote sustainability.